Insights from the Absorption Coefficient for the Development of Polarizable (Multipole) Force Fields
- PMID: 40733210
- PMCID: PMC12300768
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30142941
Insights from the Absorption Coefficient for the Development of Polarizable (Multipole) Force Fields
Abstract
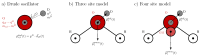
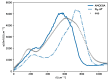
We present a detailed examination of the absorption coefficients in the THz region for different water models using different types of potentials: the non-polarizable SPC/E, the Drude-polarizable SWM4-NDP and OPC3-pol, IPOL-0.13 and the multipole AMOEBA14 water. The primary focus is on understanding the interplay between permanent and induced dipole moments and their influence on the THz spectrum. Although the induced dipoles strongly contribute to the peak at 200 cm-1, merely increasing the induced dipole moments does not improve the agreement with experiments. We aim to investigate the behavior of the intensity at 200 cm-1 depending on the water model. Furthermore, we dissect the THz spectra of the water models into distinct contributions to gain more insight into the inter- and intramolecular interactions. Intermolecular interactions significantly contribute to the low-frequency peak, while the peak observed at 600 cm-1 can be adequately attributed to intramolecular dipole-dipole interactions.
Keywords: computational spectroscopy; induced dipoles; terahertz spectroscopy; water.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Zasetsky A.Y., Lileev A.S., Lyashchenko A.K. Molecular dynamic simulations of terahertz spectra for water-methanol mixtures. Mol. Phys. 2010;108:649–656. doi: 10.1080/00268971003657086. - DOI
-
- Cherkasova O., Nazarov M., Konnikova M., Shkurinov A. THz spectroscopy of bound water in glucose: Direct measurements from crystalline to dissolved state. J. Infrared Millim. 2020;41:1057–1068. doi: 10.1007/s10762-020-00684-4. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

