Integrating Molecular Dynamics, Molecular Docking, and Machine Learning for Predicting SARS-CoV-2 Papain-like Protease Binders
- PMID: 40733251
- PMCID: PMC12300542
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30142985
Integrating Molecular Dynamics, Molecular Docking, and Machine Learning for Predicting SARS-CoV-2 Papain-like Protease Binders
Abstract
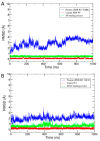
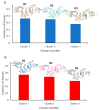
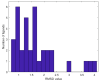
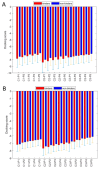
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) produced devastating health and economic impacts worldwide. While progress has been made in vaccine development, effective antiviral treatments remain limited, particularly those targeting the papain-like protease (PLpro) of SARS-CoV-2. PLpro plays a key role in viral replication and immune evasion, making it an attractive yet underexplored target for drug repurposing. In this study, we combined machine learning, molecular dynamics, and molecular docking to identify potential PLpro inhibitors in existing drugs. We performed long-timescale molecular dynamics simulations on PLpro-ligand complexes at two known binding sites, followed by structural clustering to capture representative structures. These were used for molecular docking, including a training set of 127 compounds and a library of 1107 FDA-approved drugs. A random forest model, trained on the docking scores of the representative conformations, yielded 76.4% accuracy via leave-one-out cross-validation. Applying the model to the drug library and filtering results based on prediction confidence and the applicability domain, we identified five drugs as promising candidates for repurposing for COVID-19 treatment. Our findings demonstrate the power of integrating computational modeling with machine learning to accelerate drug repurposing against emerging viral targets.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; drug repurposing; machine learning; molecular docking; molecular dynamics; papain-like protease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Discovery of SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease inhibitors through machine learning and molecular simulation approaches.Drug Discov Ther. 2025 Jul 4;19(3):189-199. doi: 10.5582/ddt.2025.01034. Epub 2025 Jun 27. Drug Discov Ther. 2025. PMID: 40571587
-
Statine-based peptidomimetics as SARS-CoV-2 Papain-like protease inhibitors: in Silico and in vitro studies.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 20;15(1):26319. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11599-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40685447 Free PMC article.
-
Generative adversarial network (GAN) model-based design of potent SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors using the electron density of ligands and 3D binding pockets: insights from molecular docking, dynamics simulation, and MM-GBSA analysis.Mol Divers. 2025 Aug;29(4):3059-3075. doi: 10.1007/s11030-024-11047-9. Epub 2024 Nov 30. Mol Divers. 2025. PMID: 39613993
-
AI-driven covalent drug design strategies targeting main protease (mpro) against SARS-CoV-2: structural insights and molecular mechanisms.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2025 Jul;43(11):5436-5464. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2024.2308769. Epub 2024 Jan 29. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2025. PMID: 38287509 Review.
-
A Review of In Silico Research, SARS-CoV-2, and Neurodegeneration: Focus on Papain-Like Protease.Neurotox Res. 2022 Oct;40(5):1553-1569. doi: 10.1007/s12640-022-00542-2. Epub 2022 Aug 2. Neurotox Res. 2022. PMID: 35917086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rudrapal M., Khairnar S.J., Jadhav A.G. Drug Repurposing—Hypothesis, Molecular Aspects and Therapeutic Applications. IntechOpen; London, UK: 2020. Drug Repurposing (DR): An Emerging Approach in Drug Discovery.
-
- Bakshi A., Gangopadhyay K., Basak S., De R.K., Sengupta S., Dasgupta A. Integrating state-space modeling, parameter estimation, deep learning, and docking techniques in drug repurposing: A case study on COVID-19 cytokine storm. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assn. 2025:ocaf035. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocaf035. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

