Unveiling the Solvent Effect: DMSO Interaction with Human Nerve Growth Factor and Its Implications for Drug Discovery
- PMID: 40733301
- PMCID: PMC12300743
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30143030
Unveiling the Solvent Effect: DMSO Interaction with Human Nerve Growth Factor and Its Implications for Drug Discovery
Abstract
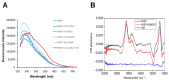
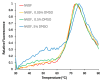
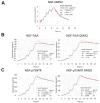
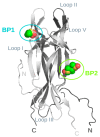
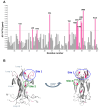
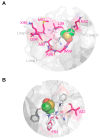
Background: The Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) is essential for neuronal survival and function and represents a key therapeutic target for pain and inflammation-related disorders, as well as for neurodegenerative diseases. Small-molecule antagonists of human NGF (hNGF) offer advantages over monoclonal antibodies, including oral availability and reduced immunogenicity. However, their development is often hindered by solubility challenges, necessitating the use of solvents like dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). This study investigates whether DMSO directly interacts with hNGF and affects its receptor-binding properties. Methods: Integrative/hybrid computational and experimental biophysical approaches were used to assess DMSO-NGF interaction by combining machine-learning tools and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR), Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, Differential Scanning Fluorimetry (DSF) and Grating-Coupled Interferometry (GCI). These techniques evaluated binding affinity, conformational stability, and receptor-binding dynamics. Results: Our findings demonstrate that DMSO binds hNGF with low affinity in a specific yet non-disruptive manner. Importantly, DMSO does not induce significant conformational changes in hNGF nor affect its interactions with its receptors. Conclusions: These results highlight the importance of considering solvent-protein interactions in drug discovery, as these low-affinity yet specific interactions can affect experimental outcomes and potentially alter the small molecules binding to the target proteins. By characterizing DMSO-NGF interactions, this study provides valuable insights for the development of NGF-targeting small molecules, supporting their potential as effective alternatives to monoclonal antibodies for treating pain, inflammation, and neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: Differential Scanning Fluorimetry (DSF); Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy; Grating-Coupled Interferometry (GCI); HADDOCK; Nerve Growth Factor (NGF); Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR); Protenix; dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO); drug discovery; solvent effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

