Cyclodextrins as Multifunctional Platforms in Drug Delivery and Beyond: Structural Features, Functional Applications, and Future Trends
- PMID: 40733310
- PMCID: PMC12299055
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30143044
Cyclodextrins as Multifunctional Platforms in Drug Delivery and Beyond: Structural Features, Functional Applications, and Future Trends
Abstract
Cyclodextrins (CDs) are cyclic oligosaccharides capable of forming inclusion complexes with various guest molecules, enhancing solubility, stability, and bioavailability. This review outlines the structural features of native CDs and their chemically modified derivatives, emphasizing the influence of functionalization on host-guest interactions. Synthetic approaches for CD derivatization are summarized, with attention to recent developments in stimuli-responsive systems and targeted drug delivery. Analytical techniques commonly employed for characterizing CD complexes, such as spectroscopy, thermal analysis, and molecular modeling, are briefly reviewed. Applications in pharmaceutical formulations are discussed, including inclusion complexes, CD-based conjugates, and nanocarriers designed for solubility enhancement, controlled release, and site-specific delivery. Special consideration is given to emerging multifunctional platforms with biomedical relevance. The regulatory status of CDs is addressed, with reference to FDA- and EMA-approved formulations. Safety profiles and toxicological considerations associated with chemically modified CDs, particularly for parenteral use, are highlighted. This review presents an integrative perspective on the design, characterization, and application of CD-based systems, with a focus on translational potential and current challenges in pharmaceutical development.
Keywords: inclusion complexes; nanocarriers; stimuli-responsive systems.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




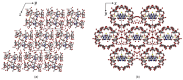








Similar articles
-
A Review of Formulation Strategies for Cyclodextrin-Enhanced Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs) and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLCs).Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 6;26(13):6509. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136509. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in cancer therapy: a critical review of β-cyclodextrins conjugated nanoparticle delivery systems as molecularly targeted therapies.Int J Pharm. 2025 Sep 15;682:125937. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2025.125937. Epub 2025 Jul 8. Int J Pharm. 2025. PMID: 40639634 Review.
-
Recent Advances in Cyclodextrin-Based Nanoscale Drug Delivery Systems.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2024 Nov-Dec;16(6):e1995. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1995. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39480078 Review.
-
Multifunctional application of supramolecular cucurbiturils as encapsulating hosts in drug delivery: A review.Int J Pharm. 2025 Aug 20;681:125801. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2025.125801. Epub 2025 Jun 7. Int J Pharm. 2025. PMID: 40490114 Review.
-
Liposomes incorporating cyclodextrins as a promising drug delivery system to augment the bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs.J Liposome Res. 2025 Sep;35(3):312-320. doi: 10.1080/08982104.2025.2473335. Epub 2025 Mar 6. J Liposome Res. 2025. PMID: 40047408 Review.
Cited by
-
Avibactam-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes: Computational and Thermodynamic Insights for Drug Delivery, Detection, and Environmental Scavenging.Molecules. 2025 Aug 18;30(16):3401. doi: 10.3390/molecules30163401. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40871555 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential of Amphiphilic Cyclodextrins as Carriers for Therapeutic Purposes: A Short Overview.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Aug 21;17(8):1086. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17081086. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40871103 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Villiers A. Sur la transformation de la fécule en dextrine par le ferment butyrique. Bull. Société Chim. Paris. 1891;45:468–470.
-
- Crini G. The contribution of Franz Schardinger to cyclodextrins: A tribute on the occasion of the centenary of his death. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2020;97:19–28. doi: 10.1007/s10847-020-00990-3. - DOI
-
- Cunha J.S., Pacheco F.C., Martins C.C.N., Pacheco A.F.C., Tribst A.A.L., Leite Junior B.R.C. Use of ultrasound to improve the activity of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase in the producing of beta-cyclodextrins: Impact on enzyme activity, stability and insights into changes on enzyme macrostructure. Food Res. Int. 2024;191:114662. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2024.114662. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ogunbadejo B.A., Al-Zuhair S. Bioconversion of starch to Cyclodextrin using Cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase immobilized on metal organic framework. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2023;53:102878. doi: 10.1016/j.bcab.2023.102878. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

