Reduced Glutathione in Modulation of Salt Stress on Sour Passion Fruit Production and Quality
- PMID: 40733387
- PMCID: PMC12298233
- DOI: 10.3390/plants14142149
Reduced Glutathione in Modulation of Salt Stress on Sour Passion Fruit Production and Quality
Abstract
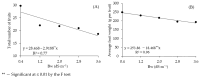
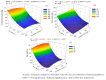
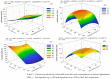
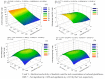
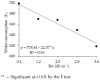
This study evaluated the effects of reduced glutathione (GSH) application on the production and quality of sour passion fruit irrigated with brackish water in the semi-arid region of Paraíba, Brazil. The experiment was conducted in drainage lysimeters under greenhouse conditions at the Center of Technology and Natural Resources of the Federal University of Campina Grande (UFCG). Treatments combined five levels of electrical conductivity of brackish irrigation water (Bw: 0.4, 1.2, 2.0, 2.8, and 3.6 dS m-1) and four GSH concentrations (0, 40, 80, and 120 mg L-1), arranged in a randomized block design with three replicates. Salinity levels above 0.4 dS m-1 negatively affected fruit production and post-harvest quality of 'BRS GA1' sour passion fruit. Foliar application of 120 mg L-1 GSH increased fruit yield, while 74 mg L-1 GSH mitigated salt stress effects on production and pulp chemical quality. The 'BRS GA1' cultivar was highly sensitive to salinity, showing a 26.9% yield reduction per unit increase in Bw electrical conductivity above 0.4 dS m-1. The results suggest that GSH can alleviate salt stress damage, improving crop productivity and fruit quality under semi-arid conditions.
Keywords: Passiflora edulis Sims; oxidative stress; salinity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Effects of Irrigation Water Salinity on the Synthesis of Photosynthetic Pigments, Gas Exchange, and Photochemical Efficiency of Sour Passion Fruit Genotypes.Plants (Basel). 2023 Nov 18;12(22):3894. doi: 10.3390/plants12223894. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38005791 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of Wild Passion Fruit at Different Ripening Stages Under Irrigated and Rainfed Cultivation Systems.Plants (Basel). 2025 Jul 11;14(14):2147. doi: 10.3390/plants14142147. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40733385 Free PMC article.
-
Foliar Applications of Salicylic Acid on Boosting Salt Stress Tolerance in Sour Passion Fruit in Two Cropping Cycles.Plants (Basel). 2023 May 18;12(10):2023. doi: 10.3390/plants12102023. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37653940 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Promotion of Ca2+ Accumulation in Roots by Exogenous Brassinosteroids as a Key Mechanism for Their Enhancement of Plant Salt Tolerance: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 9;24(22):16123. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216123. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003311 Free PMC article.
References
-
- dos Santos V.A., Ramos J.D., Laredo R.R., dos Reis Silva F.O., Chagas E.A., Pasqual M. Produção e qualidade de frutos de maracujazeiro-amarelo provenientes do cultivo com mudas em diferentes idades. Rev. De Ciências Agroveterinárias. 2017;16:33–40. doi: 10.5965/223811711612017033. - DOI
-
- Bornal D.R., Silvestrini M.M., Pio L.A.S., Costa A.C., Peche P.M., Ramos M.C.P. Brazilian position in the international fresh fruit trade network. Rev. Bras. De Frutic. 2021;43:e021. doi: 10.1590/0100-29452021021. - DOI
-
- Freire J.L.d.O., Nascimento G.d.S., Medeiros A.K.d.A. Teores e acúmulos de nutrientes em mudas de maracujazeiros sob salinidade hídrica e uso de urina de vaca. Nativ. Pesqui. Agrárias E Ambient. 2020;8:464–475. doi: 10.31413/nativa.v8i4.10103. - DOI
-
- Sousa H.C., Sousa G.G., Viana T.V.A., Pereira A.P.A., Lessa C.I.N., Souza M.V.P., Guilherme J.M.S., Góes G.F., Alves F.G.S., Gomes S.P., et al. Bacillus aryabhattai mitigates the effects of salt and water stress on the agronomic performance of maize under an agroecological system. Agriculture. 2023;13:1150. doi: 10.3390/agriculture13061150. - DOI
-
- Sousa M.G., Araújo J.K.S., Ferreira T.O., Andrade G.R.P., Araújo Filho J.C., Fracetto F.J.C., Lima G.K., Sousa Júnior V. Long-term effects of irrigated agriculture on Luvisol pedogenesis in semi-arid region, northeastern Brazil. Catena. 2021;206:105529. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2021.105529. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

