Green Extract from Pre-Harvest Tobacco Waste as a Non-Conventional Source of Anti-Aging Ingredients for Cosmetic Applications
- PMID: 40733429
- PMCID: PMC12300879
- DOI: 10.3390/plants14142189
Green Extract from Pre-Harvest Tobacco Waste as a Non-Conventional Source of Anti-Aging Ingredients for Cosmetic Applications
Abstract
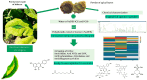
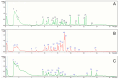
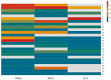
The cigarette production from Nicotiana tabacum generates significant amounts of waste, with an estimated 68.31 million tons of pre- and post-harvest waste discarded annually. The pre-harvest waste includes the upper parts of the plant, inflorescences, and bracts, which are removed to help the growth of the lower leaves. This study explores the potential of apical leaves from Nicotiana tabacum var. Virginia, discarded during the budding stage (pre-harvest waste). The leaves were extracted using environmentally friendly solvents (green solvents), including distilled water (DW) and two natural deep eutectic solvents (NaDESs), one consisting of simple sugars, fructose, glucose, and sucrose (FGS) and the other consisting of choline chloride and urea (CU). The anti-inflammatory and anti-aging potential of these green extracts was assessed by the inhibition of key enzymes related to skin aging. The xanthine oxidase and lipoxygenase activities were mostly inhibited by CU extracts with IC50 values of 63.50 and 8.0 μg GAE/mL, respectively. The FGS extract exhibited the greatest hyaluronidase inhibition (49.20%), followed by the CU extract (33.20%) and the DW extract (20.80%). Regarding elastase and collagenase inhibition, the CU extract exhibited the highest elastase inhibition, while all extracts inhibited collagenase activity, with values exceeding 65%. Each extract had a distinct chemical profile determined by LC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS and spectrophotometric methods, with several shared compounds present in different proportions. CU extract is characterized by high concentrations of rutin, nicotiflorin, and azelaic acid, while FGS and DW extracts share major compounds such as quinic acid, fructosyl pyroglutamate, malic acid, and gluconic acid. Ames test and Caenorhabditis elegans assay demonstrated that at the concentrations at which the green tobacco extracts exhibit biological activities, they did not show toxicity. The results support the potential of N. tabacum extracts obtained with NaDESs as antiaging and suggest their promising applications in the cosmetic and cosmeceutical industries.
Keywords: NaDES; Nicotiana tabacum L.; anti-aging; anti-inflammatory; cosmetics; pre-harvest waste.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Preliminary Analysis of Bilberry NaDES Extracts as Versatile Active Ingredients of Natural Dermocosmetic Products: In Vitro Evaluation of Anti-Tyrosinase, Anti-Hyaluronidase, Anti-Collagenase, and UV Protective Properties.Plants (Basel). 2025 Aug 1;14(15):2374. doi: 10.3390/plants14152374. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40805723 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NADESs) for the Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) Leaves: A Semi-Quantitative Analysis Using High Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography.Molecules. 2025 Jun 17;30(12):2620. doi: 10.3390/molecules30122620. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40572583 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotiana tabacum Leaf Waste: Morphological Characterization and Chemical-Functional Analysis of Extracts Obtained from Powder Leaves by Using Green Solvents.Molecules. 2023 Feb 1;28(3):1396. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031396. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36771071 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Datos Argentina. Agroindustria. Tabaco. 2025. [(accessed on 11 February 2025)]. Available online: https://datos.gob.ar/ro/dataset/agroindustria-tabaco---produccion.
-
- Cooperation Centre for Scientific Research Relative to Tobacco (CORESTA) [(accessed on 6 March 2025)]. Available online: https://www.coresta.org/good-agricultural-practices-gap-guidelines-29207....
-
- Diana N.E., Jamil A.H., Yogi Y.A., Nugraheni S.D., Verona L. Improving the production and quality of Virginia tobacco through topping and suckering: A Review. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022;974:012020. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/974/1/012020. - DOI
-
- Cosmetic Ingredient Database (CosIng) of the European Commission. [(accessed on 2 February 2025)]. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32022D0677.
Grants and funding
- PIUNT 2022-G727 Project/National University of Tucumán
- Fundación Williams 2023/Fundación Williams
- Fondos complementarios para proyectos de investigación con impacto en el territorio argentino and Biolates network "P320RT0186-Sustainable use of Ibero-American vegetable biomass resources in cosmetics"/Programa Iberoamericano de Ciencia y Tecnología para el Desarrollo
- CONICET-PUE 2018-0011 Project and PIP 3001 Project/Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas
- (PICT-2020-3970 and PICT-2021-CAT-II-00132/Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Técnica
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

