Real-World Treatment Efficacy and Safety Profile of Sofosbuvir- and Velpatasvir-Based HCV Treatment in South Korea: Multicenter Prospective Study
- PMID: 40733566
- PMCID: PMC12300531
- DOI: 10.3390/v17070949
Real-World Treatment Efficacy and Safety Profile of Sofosbuvir- and Velpatasvir-Based HCV Treatment in South Korea: Multicenter Prospective Study
Abstract
Background: The advent of direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) has marked a significant milestone in the therapeutic landscape of hepatitis C, greatly improving treatment efficacy. A therapeutic regimen encompassing sofosbuvir (SOF), velpatasvir (VEL), and voxilaprevir (VOX) has demonstrated strong efficacy across all genotypes of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) and has recently been incorporated into the Korean healthcare system. This study aimed to evaluate the real-world efficacy and safety of these antivirals in the South Korean population.
Methods: This prospective, multicenter, observational study enrolled patients with chronic HCV treated with SOF/VEL-based regimens at six hospitals between November 2022 and January 2024. DAA-naïve patients received SOF/VEL ± ribavirin for 12 weeks. Patients who had failed prior DAA therapy received SOF/VEL/VOX for 12 weeks. The primary endpoint was a sustained virological response at 12 weeks post-treatment (SVR12).
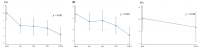
Results: Among 101 patients treated with SOF/VEL, the mean age was 64.71 years, and 40.9% were male. Genotypes 1b and 2 were identified in 40.6% and 59.4% of patients, respectively. Two patients had a history of interferon-based treatment. The mean baseline HCV RNA level was 3,088,097 IU/mL. Cirrhosis was observed in 26.7% of patients (21.8% compensated; 5.0% decompensated). Of the 101 patients, 12 were lost to follow-up. Among the 89 patients who completed follow-up, SVR12 was achieved in 100.0% (89/89), including 5 patients with decompensated cirrhosis. In the SOF/VEL/VOX group, 17 patients were treated. The mean age was 61.84 years, 29.4% were male, and four had compensated cirrhosis. One patient was lost to follow-up. SVR12 was achieved in 100.0% (16/16) of the patients who completed follow-up. No serious adverse events (≥grade 3) were reported in either group during the DAA treatment period.
Conclusions: In this first prospective real-world study in South Korea, SOF/VEL-based regimens demonstrated excellent efficacy and safety, achieving 100% SVR12 in the per-protocol population, including patients with cirrhosis and prior treatment failure.
Keywords: efficacy; hepatitis C virus; safety profile; sofosbuvir; velpatasvir; voxilaprevir.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Treatment Response in Chronic Hepatitis C Patients Receiving Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir/Voxilaprevir: A Multicenter Real-World Experience from Türkiye.Viruses. 2025 Jun 30;17(7):931. doi: 10.3390/v17070931. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40733548 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment Outcomes of Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir/Voxilaprevir in Direct-Acting Antiviral-Experienced Hepatitis C Virus Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Viruses. 2023 Jun 30;15(7):1489. doi: 10.3390/v15071489. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37515176 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and safety of sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir in patients with chronic hepatitis C previously treated with DAAs.J Hepatol. 2019 Oct;71(4):666-672. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.06.002. Epub 2019 Jun 14. J Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 31203153 Clinical Trial.
-
Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Efficacy in Pregnant People With Hepatitis C Virus.Clin Infect Dis. 2025 Apr 30;80(4):744-751. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciae595. Clin Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39688397
-
Efficacy and safety of DAA in children and adolescents with chronic HCV infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Liver Int. 2024 Mar;44(3):663-681. doi: 10.1111/liv.15827. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Liver Int. 2024. PMID: 38293756
References
-
- World Health Organization Hepatitis C Fact Sheet 2024. [(accessed on 2 April 2024)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-c.
-
- Liu C.H., Chen C.Y., Su W.W., Liu C.J., Lo C.C., Huang K.J., Chen J.J., Tseng K.C., Chang C.Y., Peng C.Y., et al. Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir plus ribavirin for Child-Pugh B and Child-Pugh C hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2021;27:575–588. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2021.0155. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

