mRNA Vaccine Development in the Fight Against Zoonotic Viral Diseases
- PMID: 40733577
- PMCID: PMC12299213
- DOI: 10.3390/v17070960
mRNA Vaccine Development in the Fight Against Zoonotic Viral Diseases
Abstract
Zoonotic diseases are transmitted from animals to humans, and they impose a significant global burden by impacting both animal and human health. It can lead to substantial economic losses and cause millions of human deaths. The emergence and re-emergence of zoonotic diseases are heavily influenced by both anthropogenic and natural drivers such as climate change, rapid urbanization, and widespread travel. Over time, the unprecedented rise of new and re-emerging zoonotic diseases has prompted the need for rapid and effective vaccine development. Following the success of the COVID-19 mRNA vaccines, mRNA-based platforms hold great promise due to their rapid design, swift development and ability to elicit robust immune responses, thereby highlighting their potential in combating emerging and pre-pandemic zoonotic viruses. In recent years, several mRNA vaccines targeting emerging and re-emerging zoonotic viral diseases, such as rabies, Nipah, Zika, and influenza, have advanced to clinical trials, demonstrating promising immunogenicity. This review explores recent advances, challenges, and future directions in developing mRNA vaccines against emerging and re-emerging zoonotic viral diseases.
Keywords: emerging zoonotic diseases; mRNA vaccine; re-emerging zoonotic diseases; vaccine development; viruses; zoonotic diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Brandon E. K. Tan, Seng Kong Tham and Chit Laa Poh were employed by the ALPS Global Holding Berhad. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
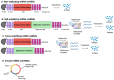
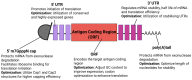
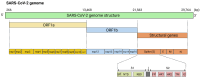
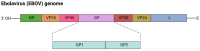


Similar articles
-
Revolutionizing immunization: a comprehensive review of mRNA vaccine technology and applications.Virol J. 2025 Mar 12;22(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12985-025-02645-6. Virol J. 2025. PMID: 40075519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing mRNA vaccines: A comprehensive review of design, delivery, and efficacy in infectious diseases.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Aug;319(Pt 3):145501. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.145501. Epub 2025 Jun 24. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40571008 Review.
-
Advancing mRNA vaccines for infectious diseases: key components, innovations, and clinical progress.Essays Biochem. 2025 May 1;69(2):EBC20253009. doi: 10.1042/EBC20253009. Essays Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40321006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The advent of clinical self-amplifying RNA vaccines.Mol Ther. 2025 Jun 4;33(6):2565-2582. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2025.03.060. Epub 2025 Apr 3. Mol Ther. 2025. PMID: 40186353 Review.
-
Advancements and Challenges in Addressing Zoonotic Viral Infections with Epidemic and Pandemic Threats.Viruses. 2025 Feb 28;17(3):352. doi: 10.3390/v17030352. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40143281 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO Newsroom-Zoonoses. Fact Sheets, 29 July 2020. [(accessed on 13 May 2025)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/zoonoses.
-
- WHO . Zoonotic Diseases: Emerging Public Health Threats in the Region. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2025. [(accessed on 13 May 2025)]. Available online: https://www.emro.who.int/about-who/rc61/zoonotic-diseases.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

