A Single Dose of Yellow Fever Vaccine Provides Long-Term Immunity in Japanese Travelers
- PMID: 40733652
- PMCID: PMC12299850
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines13070675
A Single Dose of Yellow Fever Vaccine Provides Long-Term Immunity in Japanese Travelers
Abstract
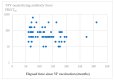
Yellow fever (YF) is an acute hemorrhagic zoonotic disease that causes severe liver damage, renal failure, and hemorrhagic shock. No antiviral treatment is available; thus, vaccination is a critical preventive measure. Although the World Health Organization (WHO) revised the guidelines regarding the need for booster vaccination for YF with the rationale that a single vaccination provides sufficient long-term immunogenicity, no studies have evaluated long-term immunity in Japanese adults who received a single dose of YF vaccine. This study evaluated the long-term persistence of immunogenicity in Japanese adults vaccinated with the YF vaccine. This observational study enrolled Japanese adults who received a single YF vaccination >5 years previously. Blood samples were collected after confirming eligibility for the study. The serum levels of anti-yellow fever virus (YFV)-neutralizing antibodies were measured using the 50% plaque reduction neutralization test (PRNT50). The 65 participants comprised 35 males and 30 females, with a median age at vaccination of 34 years. The time between YF vaccination and registration was between 5 and 26 years. All participants remained seropositive even after a long time. Statistical analysis showed no correlation between the time elapsed since YF vaccination and PRNT50. Our results indicate that a single dose of YF vaccine provides adequate long-term immunity in Japanese adults and that booster vaccinations are not routinely required. These findings strongly aid in the development of travel medicine guidelines and the optimization of vaccination strategies by reducing the usage of medical resources and simplifying the health requirements for travelers.
Keywords: anti-yellow fever virus (YFV)-neutralizing antibody; immunogenicity; long-term immunity; yellow fever (YF) vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
S. Fukushima received honoraria (lecture fees) from Sanofi K.K., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Meiji Seika Pharma Co., Ltd., and KM Biologics Co., Ltd. C.K. Lim declares no conflicts of interest associated with this study and manuscript. A. Hamada received honoraria from KM Biologics Co., Ltd., and Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Fact Sheet: Yellow Fever, WHO. 31 May 2023. [(accessed on 17 May 2025)]; Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs100/en/
-
- WHO Countries with Risk of Yellow Fever Transmission and Countries Requiring Yellow Fever Vaccination (November 2022) [(accessed on 17 May 2025)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/countries-with-risk-of-yellow-fe...
-
- Staples J.E., Gershman M., Fischer M. Yellow fever vaccine: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2010;59:1–27. - PubMed
-
- WHO Vaccines and vaccination against yellow fever. WHO position paper—June 2013. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 2013;88:269–283. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources