The Baculovirus Expression System Expresses Chimeric RHDV VLPs as Bivalent Vaccine Candidates for Classic RHDV (GI.1) and RHDV2 (GI.2)
- PMID: 40733672
- PMCID: PMC12299046
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines13070695
The Baculovirus Expression System Expresses Chimeric RHDV VLPs as Bivalent Vaccine Candidates for Classic RHDV (GI.1) and RHDV2 (GI.2)
Abstract
Background: Rabbit hemorrhagic disease (RHD) is an acute, hemorrhagic and highly lethal infectious disease caused by rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV), which causes huge economic losses to the rabbit breeding industry. Moreover, there is limited cross-protection between the two different serotypes of classic RHDV (GI.1) and RHDV2 (GI.2). The shortcomings of traditional inactivated vaccines have led to the development of novel subunit vaccines that can protect against both strains, and the VP60 capsid protein is the ideal antigenic protein. This study focused on developing a bivalent RHDV vaccine that can prevent infection with both GI.1 and GI.2 strains.
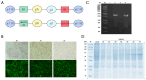
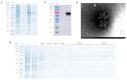
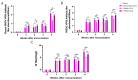
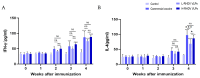
Methodology: Baculovirus vectors containing classic RHDV and RHDV2 VP60 were co-transfected with linearized baculovirus into sf9 cells and transferred to baculovirus via homologous recombination of the VP60 gene. Infected sf9 cells were lysed, and after purification via Ni-NTA chromatography, VLPs were observed using transmission electron microscopy (TEM). In order to evaluate the immunogenicity of the chimeric RHDV VLP vaccine in rabbits, the RHDV VP60-specific antibody, IL-4, IFN-γ and neutralizing antibody titers were analyzed in serum using ELISA and HI.
Results: The recombinant baculovirus system successfully expressed chimeric RHDV VLPs with a diameter of 32-40 nm. After immunization, it could produce specific antibodies, IL-4 and IFN-γ. Following the second immunization, neutralizing antibodies, determined using hemagglutination inhibition (HI) assays, were elicited.
Conclusions: These data show that the chimeric RHDV VLP bivalent vaccine for immunized New Zealand rabbits can induce humoral immunity and cellular immunity in vivo, and the immunization effect of the high-dose group is similar to that of the current commercial vaccine.
Keywords: VP60 protein; chimeric RHDV virus-like particle; rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus; recombinant baculovirus expression system; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Construction and immunogenicity of novel bivalent virus-like particles bearing VP60 genes of classic RHDV(GI.1) and RHDV2(GI.2).Vet Microbiol. 2020 Jan;240:108529. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2019.108529. Epub 2019 Nov 30. Vet Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31902498
-
Chimeric virus-like particles replacing the loop on the surface of VP60 from rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV) provide protection against two serotypes of RHDV.Vaccine. 2025 Aug 13;61:127427. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2025.127427. Epub 2025 Jul 3. Vaccine. 2025. PMID: 40614613
-
Detection of a New Recombinant Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus 2 in China and Development of Virus-like Particle-Based Vaccine.Viruses. 2025 May 16;17(5):710. doi: 10.3390/v17050710. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40431721 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity and seroefficacy of pneumococcal conjugate vaccines: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Jul;28(34):1-109. doi: 10.3310/YWHA3079. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39046101 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Camarda A., Pugliese N., Cavadini P., Circella E., Capucci L., Caroli A., Legretto M., Mallia E., Lavazza A. Detection of the new emerging rabbit haemorrhagic disease type 2 virus (RHDV2) in Sicily from rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) and Italian hare (Lepus corsicanus) Res. Vet. Sci. 2014;97:642–645. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2014.10.008. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

