An Evaluation of the Safety, Immunogenicity, and Protective Efficacy of a Combined Diphtheria-Tetanus-Acellular Pertussis, Haemophilus influenzae Type b, and ACYW135 Meningococcal Conjugate Vaccine in Murine and Rat Models
- PMID: 40733701
- PMCID: PMC12299065
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines13070724
An Evaluation of the Safety, Immunogenicity, and Protective Efficacy of a Combined Diphtheria-Tetanus-Acellular Pertussis, Haemophilus influenzae Type b, and ACYW135 Meningococcal Conjugate Vaccine in Murine and Rat Models
Abstract
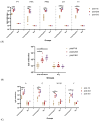
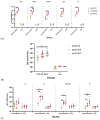
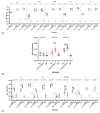
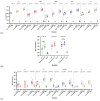
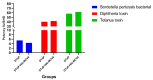
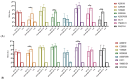
Background: The combined diphtheria-tetanus-acellular pertussis (three-component), Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib, conjugate), and ACYW135 meningococcal (conjugate) vaccine (DTaP-Hib-MCV4) offers a promising alternative to single-component vaccines, potentially simplifying immunization schedules and improving vaccination coverage. Methods: We evaluated the safety, immunogenicity, and protective efficacy of DTaP-Hib-MCV4 in animal models. Acute and long-term toxicity studies were conducted in Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats with equal numbers of male and female animals. Immunogenicity was assessed in female NIH mice and SD rats using a three-dose regimen at 14-day intervals. Orbital blood was collected 14 days post-immunization to measure IgG titers against pertussis, diphtheria, tetanus, Hib, and meningococcal antigens. The protective efficacy was determined using potency tests for the pertussis, diphtheria, and tetanus components; passive protection studies for Hib; and serum bactericidal antibody (SBA) titers against A/C/Y/W135 meningococcal serogroups. Results: Acute and repeated-dose toxicity studies in SD rats showed no signs of abnormal toxicity or irritation at either high (three doses/rat) or low (one dose/rat) doses levels. The no-observed-adverse-effect level (NOAEL) for DTaP-Hib-MCV4 was established at three doses/rat after 8 weeks of repeated intramuscular administration and a 4-week recovery period. Specific IgG antibodies against all the vaccine components were detected in animal sera at both one and three doses/rat, with no evidence of immunotoxicity. Following two-dose primary immunization in murine models, the combined vaccine elicited robust antigen-specific antibody responses, with geometric mean titers (GMTs) as follows: 1,280,000 for pertussis toxin (PT); 761,093 for filamentous hemagglutinin (FHA); 1,159,326 for pertactin (PRN); 1,659,955 for diphtheria toxoid (DT); 1,522,185 for tetanus toxoid (TT); 99 for Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib); and 25,600, 33,199, 8300, and 9051 for serogroups A, C, Y, and W135 of Neisseria meningitidis, respectively. In the rat models, three-dose primary immunization also elicited robust antigen-specific antibody responses. Protection studies demonstrated efficacy against pertussis, tetanus toxin, and diphtheria toxin challenges. In the Hib challenge study, none of the 10 animals given anti-DTaP-Hib-MCV4 antiserum developed bacteremia after the live Hib challenge (vs. 5814/0.1 mL in the negative control, p < 0.001). In addition, the SBA titers against meningococcal serogroups exceeded the protective threshold (≥1:8) in 92.2% of the immunized mice and 100% of the immunized rats. Crucially, the combined vaccine induced potent immune responses and protective efficacy, with antibody levels and protection against each component antigen comparable to or greater than those of the individual components: DTaP, Hib, and MCV4. Conclusions: These findings demonstrate that the DTaP-Hib-MCV4 combined vaccine is both safe and immunogenic, supporting its potential as a viable alternative to individual vaccines. This combined vaccine may streamline immunization programs and enhance vaccination coverage.
Keywords: ACYW135 Meningococcal Conjugate Vaccine; Combined Diphtheria-Tetanus-Acellular Pertussis; Haemophilus influenzae Type b; immunogenicity; protective efficacy; safety.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Xiuwen Sui, Yuanyuan Ji, Qingfu Xu, Bochao Wei, Zhuojun Duan, Chang Wang, Ying Yang, Jiayu Zhao, and Tao Zhu were employed by the company CanSino Biologics Inc. Zhujun Shao and Hairui Wang were employed by Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. All of the authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . DT-Based Combined Vaccines. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2014.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

