Immunogenicity, Efficacy and Twelve-Month Storage Stability Studies of a Lyophilized Rabies mRNA Vaccine
- PMID: 40733720
- PMCID: PMC12299307
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines13070743
Immunogenicity, Efficacy and Twelve-Month Storage Stability Studies of a Lyophilized Rabies mRNA Vaccine
Abstract
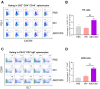
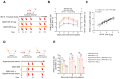
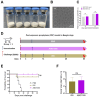
Background: Many new mRNA-based vaccine candidates in liquid mRNA-LNP formulations are under development; however, their stability limitations necessitate frozen storage, posing a significant challenge for long-term storage and transportation. Methods: In this study, an mRNA-LNP rabies vaccine, ABO1005, was prepared, freeze-dried and stored at 2-8 °C for 12-month storage stability evaluation. The immunogenicity, vaccine potency (the NIH method), and protective efficacy of ABO1005 were assessed in mice or dogs and compared to a commercialized inactivated vaccine. Results: Research conducted in mice indicated that the lyophilized vaccine exhibited comparable immunogenicity to its liquid form counterpart. Furthermore, the vaccine candidate elicited a robust humoral response lasting at least 175 days, and the specific antibody titers were not affected by the pre-administration of hyperimmune serum. In comparison to the commercialized inactivated vaccine (HDCV or PVRV), ABO1005 elicited significantly higher levels of humoral and cellular immunity. Vaccine potency testing (NIH) revealed that the potency of ABO1005 at 15 μg/dose was 8.85 IU/dose, which is substantially higher than the standard required for the lot release of rabies vaccines for current human use. In a post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) study in Beagle dogs, the lyophilized vaccine provided 100% protection for dogs following a two-dose regimen (D0-D7), whereas commercially approved inactivated vaccine offered 83% protection. After storage at 2-8 °C for 12 months, no notable changes were observed in the particle size, encapsulation efficiency, and integrity of mRNA or in the immunogenicity of the lyophilized vaccine. Conclusions: This study successfully developed a formulation and process of freeze-drying for a rabies mRNA vaccine, paving the way for future lyophilized mRNA vaccine development.
Keywords: beagles; lipid nanoparticles; long-term stability; lyophilization; mRNA vaccine; rabies.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors C.C., D.L., K.J., L.T., X.Z., X.L. (Xishan Lu), Q.H., J.Z., P.G., X.W., L.W., B.Y. were employed by the Suzhou Abogen Biosciences Co., Ltd. Authors X.L. (Xuemei Leng), C.T. were employed by the Jiangsu CuroVax Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Gibson A.D., Yale G., Corfmat J., Appupillai M., Gigante C.M., Lopes M., Betodkar U., Costa N.C., Fernandes K.A., Mathapati P., et al. Elimination of human rabies in Goa, India through an integrated One Health approach. Nat. Commun. 2022;13:2788. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30371-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ng W.M., Fedosyuk S., English S., Augusto G., Berg A., Thorley L., Haselon A.S., Segireddy R.R., Bowden T.A., Douglas A.D. Structure of trimeric pre-fusion rabies virus glycoprotein in complex with two protective antibodies. Cell Host Microbe. 2022;30:1219–1230.e1217. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2022.07.014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhai L.L., Wang H., Zhao W., Zhang S.F., Miao F.M., Cao Y., Chen C., Li Y.F., Gao J., Lv R.Y., et al. Efficacy of ormutivimab, a novel recombinant human anti-rabies monoclonal antibody, in post-exposure prophylaxis animal models. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2022;46:102267. doi: 10.1016/j.tmaid.2022.102267. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yang F., Lin S., Ye F., Yang J., Qi J., Chen Z., Lin X., Wang J., Yue D., Cheng Y., et al. Structural Analysis of Rabies Virus Glycoprotein Reveals pH-Dependent Conformational Changes and Interactions with a Neutralizing Antibody. Cell Host Microbe. 2020;27:441–453.e447. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2019.12.012. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

