Impact of Vaccination and Public Health Measures on the Severity of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Infections in China: A Systematic Review and Meta-Regression Analysis
- PMID: 40733725
- PMCID: PMC12301040
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines13070747
Impact of Vaccination and Public Health Measures on the Severity of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Infections in China: A Systematic Review and Meta-Regression Analysis
Abstract
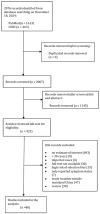
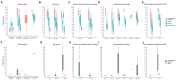
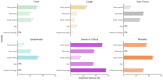
Background: Starting in early 2022, SARS-CoV-2 Omicron has driven large outbreaks in China, a predominantly infection-naive population with high inactivated vaccine coverage. This unique context provided a substantially less-confounded opportunity to evaluate how vaccination, public health, and social measures influenced severity. Methods: We systematically reviewed 86 studies (224 severity estimates) published from 2022 to 2024, reporting symptom and clinical severity outcomes (fever, cough, and sore throat; symptomatic, severe/critical, and fatal illness) of Omicron infections in China. Using meta-regression, we evaluated the associations of study setting, age group, vaccination status, predominant subvariants, and Oxford COVID-19 Government Response Tracker (OxCGRT) indices, including the Government Response Index (GRI), Containment and Health Index (CHI), and the Stringency Index (SI), with infection outcomes, adjusting for key confounders. Results: We found the primary or booster series of inactivated vaccines conferred strong protection against severe/critical illness (pooled relative risk (RR) 0.17 [95% CI: 0.09-0.33]) but did not reduce symptom frequency (RR 0.99 [95% CI: 0.95-1.02]). Each 10-unit increase in GRI or CHI was associated with 7% (95% CI: 1-12%) and 6% (95% CI: 1-10%) lower odds of symptomatic infection and 3% (95% CI: 1-4%) lower odds of severe/critical illness. Later subvariants (BA.5, BF.7, and XBB) showed 24-38% higher odds of upper respiratory symptoms versus BA.1. Conclusions: The data collection context significantly impacted severity estimates, with higher estimates from emergency hospitals. Overall, inactivated vaccines provided strong protection against severe/critical outcomes while stringent public health measures were associated with lower severity. Our findings underscore the importance of consistent and standardized protocols to produce reliable estimates of SARS-CoV-2 severity in evolving epidemiological contexts.
Keywords: COVID-19; Omicron; SARS-CoV-2; inactivated vaccines; public health measures; severity; vaccine effectiveness.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors report no other potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Tsang T.K., Sullivan S.G., Huang X., Wang C., Wang Y., Nealon J., Yang B., Ainslie K.E.C., Cowling B.J. Prior infections and effectiveness of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in test-negative studies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2024;193:1868–1881. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwae142. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

