A Combined Surgical Approach for the Treatment of a Sino-Naso-Orbital Glomangiopericytoma
- PMID: 40733863
- PMCID: PMC12225516
- DOI: 10.3390/reports6010007
A Combined Surgical Approach for the Treatment of a Sino-Naso-Orbital Glomangiopericytoma
Abstract
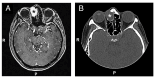
Glomangiopericytomas are a rare type of sinonasal tumors with high relapse rates. Endoscopic sinus surgery is the classical technique to remove such tumors. Here we report a case of sinonasal glomangiopericytoma with orbital extension, infrequently described in the literature. A 50 year-old woman was referred to our hospital because of a right paranasal painless swelling, which appeared 9 months ago and was slowly increasing in size since her first visit. A Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) revealed a tumor (18 × 25 × 37 mm) centered on the right ethmoidal cells, with adjacent nasal bone erosion and a right orbital invasion. The tumor was removed with a combined surgical approach (endoscopic and trans-sinusal frontal approach) after pre-surgical embolization. Based on the results of the histopathological examination, the diagnosis of a glomangiopericytoma was confirmed. The patient was discharged after one week, and an uneventful long-term follow-up.
Keywords: ENT surgery; endoscopy; glomangiopericytoma; maxillo-facial surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Zambo I., Veselý K. WHO classification of tumours of soft tissue and bone 2013: The main changes compared to the 3rd edition. Ceskoslovenska Patol. 2014;50:64–70. - PubMed
-
- Saito Y., Ohta N., Konosu-Fukaya S., Shoji F., Suzuki T., Noguchi N., Kakuta R., Ikeda R., Yamazaki M., Kusano Y., et al. Endoscopic Treatment of Sinonasal Glomangiopericytoma: A Case Report in Light of the Literature. Yonago Acta Med. 2019;62:236–239. doi: 10.33160/yam.2019.06.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
