Two Centrins and Their Posttranslational Modification Modulate the Cell Cycle of Giardia lamblia
- PMID: 40734239
- PMCID: PMC12307541
- DOI: 10.1002/mbo3.70038
Two Centrins and Their Posttranslational Modification Modulate the Cell Cycle of Giardia lamblia
Abstract
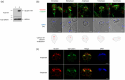
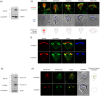
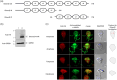
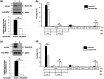
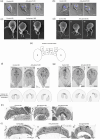
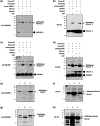
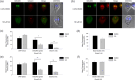
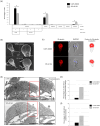
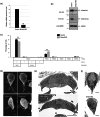
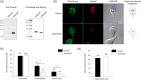
Centrins, Ca2+-binding proteins conserved in eukaryotes, are the key components of the microtubule-organizing center. Giardia lamblia possesses two centrins (GL50803_6744: centrin 1; GL50803_104685: centrin 2) localized in the basal bodies during cell division. G. lamblia centrin 2 (Glcent2) is also found in the nuclei of interphase Giardia, with its N-terminal half being necessary for this localization. Morpholino-mediated knockdown of Glcents resulted in abnormal nuclear positioning and cytokinesis, causing cell malformations, including ventral discs and flagella defects. Small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO)ylation is a posttranslational modification, which modulates several cellular processes. Here, we demonstrated that Glcents are substrates of SUMO through in vitro SUMOylation and immunoprecipitation experiments. Additionally, treatment of Giardia with ginkgolic acid, which inhibits the E1 enzyme of the SUMO pathway, and CRISPRi-mediated inhibition of G. lamblia Ubc9, the E2 conjugation enzyme involved in SUMOylation, resulted in defects in the localization of Glcents. Blocking SUMOylation resulted in the arrest of Giardia cells and conformational changes, including alterations in the ventral disc shape, posterolateral flanges, and peripheral vesicles. Taken together, we demonstrated that Glcents function in Giardia cell cycle progression and morphogenesis, with the activity of both Glcents being modulated by SUMOylation.
Keywords: Giardia lamblia; SUMOylation; cell cycle; centrin.
© 2025 The Author(s). MicrobiologyOpen published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

