miR-708-5p Attenuates Osteoarthritis Progression via Multi-Target Modulation of the NOX4/NF-κB Axis and Cartilage Homeostasis
- PMID: 40734512
- PMCID: PMC12310611
- DOI: 10.1177/19476035251361679
miR-708-5p Attenuates Osteoarthritis Progression via Multi-Target Modulation of the NOX4/NF-κB Axis and Cartilage Homeostasis
Abstract
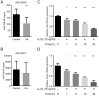
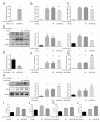
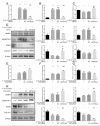
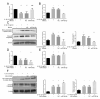
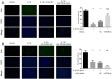
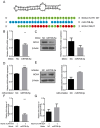
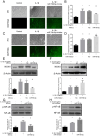
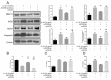
ObjectiveTo investigate the novel role of miR-708-5p in osteoarthritis (OA) and its potential as a therapeutic target through regulation of NOX4/NF-κB signaling.MethodsExpression levels of miR-708-5p were analyzed in OA cartilage using GEO datasets and validated in interleukin (IL)-1β-treated primary human chondrocytes. Gain- and loss-of-function experiments were performed using miR-708-5p mimics and inhibitors to evaluate its effects on inflammation, extracellular matrix metabolism, apoptosis, and oxidative stress. Direct targeting of NOX4 by miR-708-5p was confirmed through bioinformatic prediction, luciferase reporter assays, and rescue experiments.ResultsmiR-708-5p was significantly downregulated in OA cartilage and IL-1β-treated chondrocytes. Overexpression of miR-708-5p attenuated IL-1β-induced inflammatory responses by suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor [TNF]-α), inhibiting matrix-degrading enzymes (MMP3, ADAMTS-4), and enhancing anabolic factors (COL2A1, SOX9). miR-708-5p protected against chondrocyte apoptosis by regulating Bcl2/BAX and caspase-3 expression. It also increased chondrocyte proliferation in EdU assays and reduced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Mechanistically, miR-708-5p directly inhibited NOX4, reducing ROS generation and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) activation. NOX4 overexpression reversed the protective effects of miR-708-5p, confirming the functional significance of this regulatory axis.ConclusionmiR-708-5p is downregulated in OA and exerts chondroprotective effects. These findings suggest that restoring miR-708-5p expression may effectively suppress the NOX4/NF-κB axis and modulate chondrocyte inflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis, and matrix degradation.
Keywords: NOX4/NF-κB signaling; cartilage homeostasis; chondrocyte inflammation; miR-708-5p; osteoarthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exosomes of Human Fetal Cartilage Progenitor Cells (hFCPCs) Inhibited Interleukin-1β (IL-1β)-Induced Osteoarthritis Phenotype via miR-125b-5p In Vitro.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2025 Jul;22(5):691-703. doi: 10.1007/s13770-025-00720-1. Epub 2025 May 15. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2025. PMID: 40372627
-
MicroRNA-322 Attenuates Cartilage Matrix Degradation in Osteoarthritis via Direct Suppression of TRAF3.Cartilage. 2025 Sep;16(3):357-365. doi: 10.1177/19476035231213207. Epub 2023 Dec 14. Cartilage. 2025. PMID: 38098174 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulated miR-374a-5p drives psoriasis pathogenesis through WIF1 downregulation and Wnt5a/NF-κB activation.Cell Signal. 2024 Jul;119:111171. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111171. Epub 2024 Apr 9. Cell Signal. 2024. PMID: 38604345
-
Kruppel-like factor 9 may regulate the inflammatory injury of chondrocytes by affecting NF-κB signaling.J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 Jun 18;20(1):599. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-05974-y. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 40533763 Free PMC article.
-
p-Synephrine Loaded by Injectable Gelma Hydrogel Ameliorates Cartilage Degeneration in Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting the MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Pathways.Biol Pharm Bull. 2025;48(6):882-894. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b25-00139. Biol Pharm Bull. 2025. PMID: 40545361
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

