Prognostic value of circulating uric acid in gastrointestinal cancers, a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40734811
- PMCID: PMC12301538
- DOI: 10.22037/ghfbb.v18i1.2965
Prognostic value of circulating uric acid in gastrointestinal cancers, a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Aim: Thus, this meta-analysis was performed to assess the prognostic value of serum uric acid in patients with gastrointestinal cancers (GI).
Background: There is growing evidence that high serum uric acid may be used as a potential prognostic marker in gastrointestinal malignancies. However, there are inconsistencies in the reported findings.
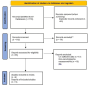
Methods: Related studies were identified by searching the following databases: PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and Scopus, independently up until 30 October 2023. Relevant analyses were carried out to deal with heterogeneity in the data. According to the inclusion criteria, we used English original papers reporting prognostic value of serum/plasma uric acid to determine hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) in patients with GI cancers. Pooled hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were used to ascertain the association of uric acid levels with gastrointestinal cancer (GI) risk. The inconsistency index (I2) was used to calculate the level of heterogeneity among the selected studies. The quality of each study was evaluated by Newcastle-OTTAWA Scales (NOS).
Results: A total of 9 papers with 95.285 patients were included in this meta-analysis. The findings indicated a significant association between serum uric acid and poor prognosis in patients with gastrointestinal cancers (HR=1.477, 95% CI 1.165-1.873, P= 0.001). Further, in Subgroup analysis we found that patients would have poor survival rate among different cut-offs of uric acid, ≥ 5mg/dl, HR= 1.403, 95% CI=1.150-1.711, P=0.001 vs cut-off <5mg/dl, HR=1.54, 95% CI=1.140-2.063, P=0.005.
Conclusion: Serum uric acid level is significantly linked to survival outcomes in patients with gastrointestinal cancers. Serum uric acid levels may be an effective prognostic marker associated with clinical outcomes in patients with gastrointestinal cancers. Given the small number of studies included in this meta-analysis and high heterogeneity, we suggest that a more comprehensive study is required to achieve more robust results.
Keywords: Gastrointestinal cancers; Hazard ratio; Prognosis; Survival; Uric acid.
© 2025, Gastroenterology and Hepatology From Bed to Bench (GHFBB).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical symptoms, signs and tests for identification of impending and current water-loss dehydration in older people.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Apr 30;2015(4):CD009647. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009647.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25924806 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidants for female subfertility.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Aug 5;(8):CD007807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007807.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 28;7:CD007807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007807.pub3. PMID: 23913583 Updated.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
References
-
- LI H. Global Health Estimates 2016: Deaths by cause, age, sex, by country and by region, 2000–2016. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018.
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
-
- Maiuolo J, Oppedisano F, Gratteri S, Muscoli C, Mollace V. Regulation of uric acid metabolism and excretion. Int J Cardiol. 2016;213:8–14. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
