Research progress of regulating intestinal flora by traditional Chinese medicine in treating coronary heart disease
- PMID: 40734911
- PMCID: PMC12301970
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chmed.2025.04.007
Research progress of regulating intestinal flora by traditional Chinese medicine in treating coronary heart disease
Abstract
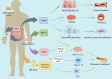
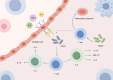
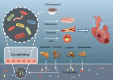
Coronary atherosclerotic heart disease is a major cardiovascular condition driven by atherosclerosis, distinguished by chronic inflammation and dysregulated lipid metabolism. The gut microbiota plays an essential role in human health and disease, with research indicating a strong association between gut microbial metabolism and the development and progression of coronary heart disease. This article provides a review of the relationship between gut microbiota and coronary heart disease, as well as the mechanisms by which traditional Chinese medicine regulates digestive tract microbiota to treat coronary heart disease, which systematically explains how the gut microbiota, through metabolic products and immune regulation, contributes to the occurrence and progression of coronary heart disease, and summarizes recent advances in research on traditional Chinese medicine's regulation of gut microbiota for treating coronary heart disease. It aims to provide further reference and insights for exploring the relationship between gut microbiota and coronary heart disease, as well as traditional Chinese medicine approaches for treating coronary heart disease.
Keywords: coronary heart disease; intestinal flora; mechanism of action; therapeutic effect; traditional Chinese medicine.
© 2025 Tianjin Press of Chinese Herbal Medicines. Published by ELSEVIER B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing finacial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Influence of Gut Microbiota-Derived Butyrate on Intestinal Uric Acid Excretion and Hyperuricemia Regulation by Cichorium intybus L.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 3;26(13):6413. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136413. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650188 Free PMC article.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
Prevention and Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease Via the Regulation of the Gut Microbiota With Traditional Chinese Medicine.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Nov;30(11):e70101. doi: 10.1111/cns.70101. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 39508315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hesperidin improves cardiac fibrosis induced by β-adrenergic activation through modulation of gut microbiota.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2025 Jun;392(6):103578. doi: 10.1016/j.jpet.2025.103578. Epub 2025 Apr 7. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2025. PMID: 40378637
-
Radiation-induced injury and the gut microbiota: insights from a microbial perspective.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025 Jun 16;18:17562848251347347. doi: 10.1177/17562848251347347. eCollection 2025. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40535532 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adilah F.A., Girish D., Fergal O.G. The gut microbiome and cardiovascular disease: Current knowledge and clinical potential. American Journal of Physiology. 2019;317(5):H923–H938. - PubMed
-
- Cai W., Wei X.F., Zhang J.R., Tao L., Li D., Zhang K., et al. Acupuncture ameliorates depression-like behavior of poststroke depression model rats through the regulation of gut microbiota and NLRP3 inflammasome in the colon. NeuroReport. 2024;35(14):883–894. - PubMed
-
- Cao L.H., Ni H.X., Gong X.X., Zang Z.Y., Chang H. Chinese Herbal medicines for coronary heart disease: Clinical evidence, pharmacological mechanisms, and the interaction with gut microbiota. Drugs. 2024;84(2):179–202. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources