Biocomposites of Enzymes and Covalent Organic Frameworks: A Novel Family of Heterogenous Biocatalysis
- PMID: 40735016
- PMCID: PMC12301865
- DOI: 10.1021/cbe.5c00013
Biocomposites of Enzymes and Covalent Organic Frameworks: A Novel Family of Heterogenous Biocatalysis
Abstract
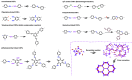
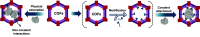
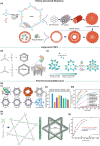
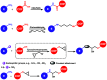
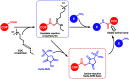
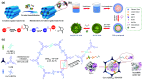
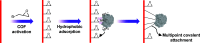
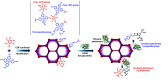
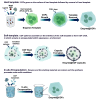
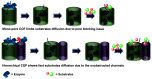
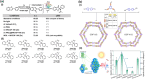
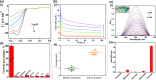
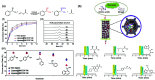
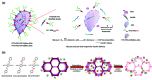
Enzymatic catalysis is a green alternative to chemical catalysis, with high activity and selectivity toward the target products in very mild reaction conditions. However, the three-dimensional active structure of an enzyme is very fragile and highly sensitive to external variables such as temperature, pH, and chemical stressors, severely limiting the application range of natural enzymes. A viable solution is to immobilize enzymes within solid porous matrices. Among the most recently developed porous materials are covalent organic frameworks (COFs). They hold great potential as enzyme carriers, as they are nontoxic, light, and highly porous crystalline polymers. Unlike metal-organic frameworks, COFs do not carry a risk of any potential metal-ion leakage, and they offer long-term water/chemical stability. COFs exhibit larger surface areas and variety in their structural/chemical design compared to other conventional supports, like silica or polymers. In this Review, we offer for the first time a comprehensive overview of all the synthetic methods created so far for biocomposites of enzymes and COFs, together with an in-depth discussion of their design principles. We then focus on the critical synthetic parameters that may affect the chemistry of the resultant biocomposites, which find applications in biocatalysis, photoenzymatic catalysis, biosensing, chiral resolution, and stimuli-responsive release. The review ends by discussing the challenges and future opportunities related to the immobilization methods as well as the practical applications. We hope that this Review might guide researchers in developing more advanced encapsulation strategies to boost the enzymatic performance in real-world applications.
Keywords: Catalysis; Chiral Resolution; Covalent Organic Frameworks; Enzyme Immobilization; Immobilization Mechanisms; Sensing.
© 2025 The Authors. Co-published by Zhejiang University and American Chemical Society.
Figures








References
-
- Bell E. L., Finnigan W., France S. P., Green A. P., Hayes M. A., Hepworth L. J., Lovelock S. L., Niikura H., Osuna S., Romero E., Ryan K. S., Turner N. J., Flitsch S. L.. Biocatalysis. Nature Reviews Methods Primers. 2021;1(1):46. doi: 10.1038/s43586-021-00044-z. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
