Judo exercises increase emotional expression, self-control, and psychological resilience
- PMID: 40735181
- PMCID: PMC12305810
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1632095
Judo exercises increase emotional expression, self-control, and psychological resilience
Abstract
Background: The extant research on judo sports has principally concentrated on the physiological effects of training. Conversely, there has been limited attention paid to studies on psychological resilience, self-control, and emotional expression levels. The present study examined the effects of Judo exercises on psychological resilience, self-control, and emotional expression levels in healthy male subjects.
Methods: The present study comprised 50 healthy, sedentary male subjects. The subjects were randomly divided into two groups: one group participated in judo training (JT) and the other group served as the control group (CON). The sample sizes for the JT and CON groups were both 25. The JT group underwent judo training, while the CON group maintained their usual lifestyle. The Brief Psychological Resilience Scale, the Multidimensional Brief Self-Control Scale, and the Berkeley Emotion Expression Scale were administered prior to and following the 6-week training period.
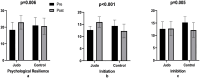
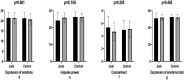
Results: The study demonstrated that a 6-week judo training regimen exerted a significant effect on the psychological resilience score (e.s. = 1.047, p < 0.001), while no such effect was observed in the Control group (e.s. = 0.0091, p = 0.751). In the context of self-control levels, an effect was observed on the Initiation sub-dimension (e.s. = 1, 739, p < 0.001), yet no effect was found on the Inhibition dimension (e.s. = 0.052, p = 0.892). In the control group, a significant decrease was identified in the Initiation sub-dimension (e.s. = 0, 785, p = 0.001) and Inhibition sub-dimension (e.s. = 1, 861, p < 0.001). The findings indicate that impulse power (e.s. = 0.395) and concealment (e.s. = 0.428) exerted a negligible influence on the emotional expression sub-dimensions. Conversely, psychological resilience (e.s. = 0.886) demonstrated a substantial impact.
Conclusions: The judo exercises demonstrated a favorable impact on psychological resilience, self-control, and emotional expression levels in healthy male subjects. The findings of this study may offer significant insights into the impact of judo exercises on psychological resilience, self-control, and emotion expression levels. These findings could serve as a guide for the development of future interventions and program design in the domain of sport psychology.
Keywords: combat sports; judo; mental health; psychological resilience; self-control; sport psychology.
Copyright © 2025 Köroǧlu, Yılmaz, Tan, Çelikel, Budak, Kavuran, Susuz, Barut, Ceylan, Soyer, Sezer and Şahin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Taekwondo exercises for women improve quality of life, physical self-defence skills, and psychological resilience.Front Psychol. 2025 Jul 30;16:1638975. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1638975. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40808743 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-deployment programmes for building resilience in military and frontline emergency service personnel.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Dec 6;12(12):CD013242. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013242.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34870330 Free PMC article.
-
Physical exercise training interventions for children and young adults during and after treatment for childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 31;3(3):CD008796. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008796.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27030386 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological and/or educational interventions for the prevention of depression in children and adolescents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(1):CD003380. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003380.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Dec 07;(12):CD003380. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003380.pub3. PMID: 14974014 Updated.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
References
-
- Baumeister R. F., Vohs K. D., Tice D. M. (2007). The strength model of self-control. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 16, 351–355. 10.1111/j.1467-8721.2007.00534.x - DOI
-
- Biedrzycki J., Laskowski R. (2024). The impact of judo training on the development of cognitive functions-a systematic review. Balt. J. Health Phys. Act. 16:7. 10.29359/BJHPA.16.4.0 - DOI
-
- Broussal-Derval A. (2021). Training and Conditioning for Judo. Champaign: Human Kinetics Publishers.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

