Analgesia Quality and Duration of Fentanyl and Sufentanil Added to Bupivacaine in Spinal Anesthesia in Inguinal Hernia Surgery: A Double-Blind Parallel Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 40735260
- PMCID: PMC12301504
- DOI: 10.1002/hsr2.71116
Analgesia Quality and Duration of Fentanyl and Sufentanil Added to Bupivacaine in Spinal Anesthesia in Inguinal Hernia Surgery: A Double-Blind Parallel Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background and aims: To compare the quality and duration of analgesia provided by Fentanyl and Sufentanil when added to 12-15 mg Bupivacaine 0.5% in spinal anesthesia for inguinal hernia surgery.
Methods: In the present double-blind parallel Randomized Controlled Trial (RCT), 180 patients who were candidates for elective inguinal hernia surgery were divided into three groups using balanced-block randomization. The first group received 2.5 cc Bupivacaine with 0.5 cc (25 mg) Fentanyl, the second group received 0.5 cc (2.5 micrograms) of Sufentanil with 2.5 cc Bupivacaine, and the third group received 2.5 cc Bupivacaine with 0.5 cc normal saline. The pain score was evaluated by VAS (visual analog scale) at recovery and arrival in PACU, 2, 4, 6, and 12 h after the surgery.
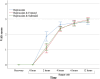
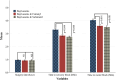
Results: A total of 60 subjects were allocated to each group. The mean (standard deviation) of pain score 2 h after surgery in Bupivacaine, Bupivacaine-Fentanyl, and Bupivacaine-Sufentanil were 1.73 (0.49), 1.10 (1.10), and 1.22 (1.25), respectively. These values 12 h after surgery were 2.76 (0.36), 2.97 (0.61), and 2.92 (0.56), respectively. The within-group comparison showed a significant increase in the pain score over time (p < 0.001). Also, the between-group comparison revealed significant differences between the three groups regarding pain scores (p = 0.030), so that the mean and standard deviation of pain score in Bupivacaine (1.67 ± 0.05) was higher than Bupivacaine-Fentanyl (1.51 ± 0.09) (p < 0.001) and Bupivacaine-Sufentanil (1.52 ± 0.08) (p < 0.001), but Bupivacaine-Fentanyl was not different from Bupivacaine-Sufentanil (p = 0.437). Results showed a significant interaction between time and intervention for pain score (p < 0.001).
Conclusions: The pain-reducing effects of Sufentanil and Fentanyl, when combined with Bupivacaine, were significantly greater than those of Bupivacaine alone. However, this effect lasts only for up to 4 h after surgery, after which their efficacy diminishes.
Keywords: Bupivacaine; Fentanyl; Sufentanil; inguinal hernia surgery; pain; randomized clinical trial.
© 2025 The Author(s). Health Science Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prolonging the duration of single-shot intrathecal labour analgesia with morphine: A systematic review.Scand J Pain. 2016 Oct;13:36-42. doi: 10.1016/j.sjpain.2016.06.010. Epub 2016 Jul 18. Scand J Pain. 2016. PMID: 28850533
-
Safety and efficacy of low-dose esketamine weakly opioidized anesthesia in elderly patients with lumbar spinal stenosis undergoing surgery: a prospective, double-blind randomized controlled trial.BMC Anesthesiol. 2025 Feb 5;25(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12871-025-02908-3. BMC Anesthesiol. 2025. PMID: 39910473 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Single dose intra-articular morphine for pain control after knee arthroscopy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 3;2016(5):CD008918. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008918.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27140500 Free PMC article.
-
The median Effective Dose (ED50) and the 95% Effective Dose (ED95) of alfentanil in inhibiting responses to cervical dilation when combined with ciprofol during hysteroscopic procedure: a prospective, double-blind, dose-finding clinical study.BMC Anesthesiol. 2025 Jul 19;25(1):353. doi: 10.1186/s12871-025-03217-5. BMC Anesthesiol. 2025. PMID: 40684098 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative Efficacy of Periarticular Fentanyl versus Ketorolac for Postoperative Pain in Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Orthop Case Rep. 2025 Jul;15(7):268-274. doi: 10.13107/jocr.2025.v15.i07.5846. J Orthop Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40635926 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meco B. C., Bermede O., Vural C., Cakmak A., Alanoglu Z., and Alkis N., “A Comparison of Two Different Doses of Morphine Added to Spinal Bupivacaine for Inguinal Hernia Repair,” Brazilian Journal of Anesthesiology (Elsevier) 66 (2016): 140–144. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharya P., Mandal M. C., Mukhopadhyay S., Das S., Pal P. P., and Basu S. R., “Unilateral Paravertebral Block: An Alternative to Conventional Spinal Anaesthesia for Inguinal Hernia Repair,” Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 54, no. 2 (2010): 246–251. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

