Targeting HASPIN kinase disrupts SR protein-mediated RNA splicing and synergizes with BCL-2 inhibitor venetoclax in AML
- PMID: 40735352
- PMCID: PMC12304681
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bneo.2025.100107
Targeting HASPIN kinase disrupts SR protein-mediated RNA splicing and synergizes with BCL-2 inhibitor venetoclax in AML
Abstract
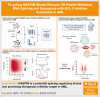
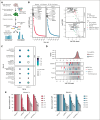
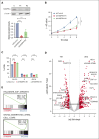
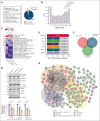
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a blood cancer complicated by acquired drug resistance, disease relapse, and low overall survival rates. Combination therapies using multiple targeted inhibitors have been effective in treating patients with AML. However, combination treatments are limited by the number of usable targets and our ability to create rational pairings using complimentary molecular mechanisms. Here, we used a human kinase domain-targeted CRISPR screen to identify histone H3-associated protein (HASPIN) kinase as a significant, understudied dependency in AML. HASPIN depletion significantly reduced growth rate, induced a cell cycle arrest, and dysregulated transcription in AML. A proteomics data mining study characterized serine and arginine repeat enriched splicing factors (SR proteins) as a major category of HASPIN kinase substrates and highlighted the role of HASPIN as a splicing regulatory kinase. Accordingly, HASPIN depletion strongly dysregulated splicing in AML cells. HASPIN inhibitor CHR-6494 effectively reduced cell viability across AML subtypes while sparing healthy cells. Furthermore, a novel combination therapy consisting of CHR-6494 and B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) inhibitor venetoclax synergistically reduced AML cell viability and resensitized venetoclax-resistant AMLs to treatment. Our study presents HASPIN kinase as a novel therapeutic target for AML, underscores an underappreciated role of HASPIN in splicing regulation, and proposes a viable combination treatment for clinical testing.
© 2025 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Fenretinide targets GATA1 to induce cytotoxicity in GATA1 positive Acute Erythroid and Acute Megakaryoblastic Leukemic cells.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Apr 15:2025.01.19.633759. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.19.633759. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39896667 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Integrated stress response activation induced by usnic acid alleviates BCL-2 inhibitor ABT-199 resistance in acute myeloid leukemia.J Adv Res. 2025 Aug;74:621-635. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.10.003. Epub 2024 Oct 9. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 39384125 Free PMC article.
-
NRF2 maintains redox balance via ME1 and NRF2 inhibitor synergizes with venetoclax in NPM1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia.Cancer Metab. 2025 Jun 18;13(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s40170-025-00401-6. Cancer Metab. 2025. PMID: 40533864 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-2 as maintenance therapy for children and adults with acute myeloid leukaemia in first complete remission.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Nov 6;2015(11):CD010248. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010248.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26544114 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024 [published correction appears in CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(2):203] CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(1):12–49.
-
- Döhner H, Wei AH, Appelbaum FR, et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2022 recommendations from an international expert panel on behalf of the ELN. Blood. 2022;140(12):1345–1377. - PubMed
-
- Döhner H, DiNardo CD, Appelbaum FR, et al. Genetic risk classification for adults with AML receiving less-intensive therapies: the 2024 ELN recommendations. Blood. 2024;144(21):2169–2173. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

