Efficacy of comprehensive rehabilitation training for elderly patients with lower limb fractures after surgery
- PMID: 40735557
- PMCID: PMC12302108
- DOI: 10.12669/pjms.41.7.12125
Efficacy of comprehensive rehabilitation training for elderly patients with lower limb fractures after surgery
Abstract
Objective: Exploring the efficacy of comprehensive rehabilitation training (CRT) for elderly patients with lower limb fractures (LLF) after surgery.
Methods: This is a single center retrospective cohort study included clinical data of 120 elderly patients with LLF who underwent surgical treatment at Dongguan Chang'an Hospital from February 2021 to August 2023. Of them, 58 patients received routine rehabilitation training (control group) and 62 patients received CRT (observation group). Range of motion of lower limb joints, activities of daily living (ADLs), pain intensity, and incidence of complications were compared between the two groups.
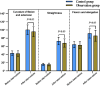
Results: After surgery, curvature, straightness, and degree of flexion and extension of the lower limb joints in both groups significantly increased, and was significantly greater in the observation group (P<0.05). Modified Barthel Index (MBI) scores of both groups significantly increased after surgery, and was significantly higher in the observation group (P<0.05). Post-surgery visual analog scale (VAS) scores of both groups significantly decreased, and were significantly lower in the observation group (P<0.05). The incidence of complications was significantly lower in the observation group than in the control group (P<0.05).
Conclusions: Implementing CRT for elderly patients with LLF can increase the range of motion of the lower limb joints, improve ADLs, alleviate pain levels, and reduce the risk of complications.
Keywords: Comprehensive rehabilitation training; Elderly patient; Lower limb fractures.
Copyright: © Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Clinical effects of extracorporeal shock wave combined with complex decongestive therapy in the treatment of lower limb lymphedema after cervical cancer surgery].Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2025 Jun 20;41(6):543-551. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501225-20250205-00051. Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40588402 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Conservative interventions for preventing clinically detectable upper-limb lymphoedema in patients who are at risk of developing lymphoedema after breast cancer therapy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Feb 13;2015(2):CD009765. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009765.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25677413 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and efficacy of low-dose esketamine weakly opioidized anesthesia in elderly patients with lumbar spinal stenosis undergoing surgery: a prospective, double-blind randomized controlled trial.BMC Anesthesiol. 2025 Feb 5;25(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12871-025-02908-3. BMC Anesthesiol. 2025. PMID: 39910473 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Ultrasound and shockwave therapy for acute fractures in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jun 23;2014(6):CD008579. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008579.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Mar 3;3:CD008579. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008579.pub4. PMID: 24956457 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Reverse shoulder arthroplasty with tuberosity healing after proximal humeral fractures and rotator cuff arthropathy: similar functional outcomes and complications in patients after 10 years follow-up.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2025 Jun 3:S1058-2746(25)00431-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2025.04.030. Online ahead of print. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2025. PMID: 40472957
References
-
- Atilgan N, Ipek B, Duman N, Orhan O, Yilmaz M. Can anterolateral thigh flap be a rescuer in lower extremity injuries? Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023;27(15):7005–7011. doi:10.26355/eurrev_202308_33272. - PubMed
-
- Xing J, Fu YH, Song Z, Wang Q, Ma T, Li M, et al. Predictive model for deep venous thrombosis caused by closed lower limb fracture after thromboprophylactic treatment. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022;26(22):8508–8522. doi:10.26355/eurrev_202211_30387. - PubMed
-
- Henkelmann R, Palke L, Schneider S, Müller D, Karich B, Mende M, et al. Impact of anti-gravity treadmill rehabilitation therapy on the clinical outcomes after fixation of lower limb fractures:A randomized clinical trial. Clin Rehabil. 2021;35(3):356–366. doi:10.1177/0269215520966857. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials