Hemodynamic homeostasis disequilibrium in critical illness
- PMID: 40735670
- PMCID: PMC12304090
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1503320
Hemodynamic homeostasis disequilibrium in critical illness
Abstract
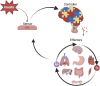
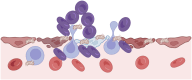
Over millions of years, the circulatory system evolved from primitive forms into a highly specialized network capable of overcoming time-distance constraints and enhancing diffusion efficiency. This structural advancement laid the physiological foundation for the regulation of hemodynamics and systemic homeostasis. Hemodynamic homeostasis is a fundamental biological process that ensures the continuous delivery of oxygen and substrates while facilitating the removal of carbon dioxide and metabolic waste. Such balance is essential for sustaining cellular metabolism and maintaining the function of vital organs throughout embryonic development and the human lifespan. Disruption of this equilibrium, primarily driven by the Host/Organ Unregulated Response (HOUR), compromises the cardiovascular-respiratory system, resulting in hemodynamic homeostasis disequilibrium. HOUR specifically targets the critical unit-a constellation of elements essential for oxygenation and cell energetics, including the microcirculation, endothelial glycocalyx, and mitochondria, impairing the oxygenation process, ultimately triggering critical illness. Although intervention targeting systemic hemodynamic variables (e.g., pressure, flow) may temporarily improve regional perfusion, restoring full homeostasis remains challenging. This is largely due to the activation of multiple positive feedback loops (e.g., coagulation cascades) and impairment of key negative feedback mechanisms (e.g., blood pressure regulation). In the presence of ongoing HOUR, inappropriate or delayed interventions may exacerbate injury and accelerate irreversible organ damage or death. Therefore, it is both essential and urgent to elucidate the initiation, recognition, progression, and modulation of hemodynamic homeostasis disequilibrium.
Keywords: HOUR (Host/Organ Unregulated Response); critical unit; hemodynamic homeostasis; hemodynamic homeostasis disequilibrium; hypoxia.
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Wang, Liu, Lian, Wang, Tong, Deng, Guo, Zhang, Chao and Yin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
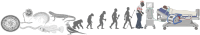

Similar articles
-
Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome.2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31613449 Free Books & Documents.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Ventilator Management(Archived).2023 Mar 27. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2023 Mar 27. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 28846232 Free Books & Documents.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

