Immunoregulatory Endothelial Cells Interact With T Cells After Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 40735785
- PMCID: PMC12398352
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.125.326145
Immunoregulatory Endothelial Cells Interact With T Cells After Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
Background: Endothelial cells (ECs) play pivotal roles in maintaining cardiac blood supply and regulating inflammation by acting as gatekeepers for immune cell activity. This study unveils a novel immunomodulatory function of cardiac ECs following myocardial infarction.
Methods: We used single-cell RNA sequencing and spatial transcriptomics to identify EC states after acute myocardial infarction in mice. Subsequently, we mimicked the cytokine environment that was predicted to induce EC activation in cell culture studies and confirmed the results in an endothelial-specific deletion mouse model.
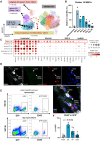
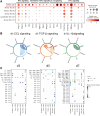
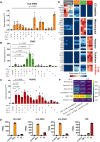
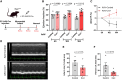
Results: Single-cell RNA sequencing analysis identified a transient myeloid CD45+CD11b+Cdh5+ immunomodulatory EC phenotype (IMEC) emerging between days 1 and 3 after myocardial infarction. IMECs derived from Cdh5+ tissue resident cells as shown by bone marrow transplantation and lineage tracing experiment. Ligand-receptor interaction predictions indicated a cytokine-mediated activation of IMECs, which we validated through in vitro experiments in cultured ECs. Notably, while cytokine treatment with IL-1β and TGF-β (transforming growth factor β) induced mesenchymal gene expression, the addition of IFN-γ (interferon γ) facilitated the transition into the immunomodulatory phenotype. IMECs exhibited an upregulation of MHC-II (major histocompatibility complex class II) genes, along with the expression of RUNX1 (runt-related transcription factor-1) and proinflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6 and IL-12. IMECs induced T-cell activation through paracrine signaling and were colocalized with T cells in vivo. Inhibition of endothelial-specific IFN-γ-signaling in mice by IFN-γ receptor 1 deletion improved the recovery after myocardial infarction.
Conclusions: These findings provide insight into the role of ECs regulating adaptive immune responses following myocardial infarction, offering potential insights into therapeutic interventions for postinfarction immunomodulation.
Keywords: T-lymphocytes; endothelial cells; infarction; inflammation; ischemia.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Comment in
-
Early Post-MI Proinflammatory Cardiac Endothelial Cells Contribute to Disease.Circ Res. 2025 Aug 29;137(6):880-881. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.125.327127. Epub 2025 Aug 28. Circ Res. 2025. PMID: 40875793 No abstract available.
References
-
- Gomez-Salinero JM, Itkin T, Rafii S. Developmental angiocrine diversification of endothelial cells for organotypic regeneration. Dev Cell. 2021;56:3042–3051. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2021.10.020 - PubMed
-
- Urbanczyk M, Zbinden A, Schenke-Layland K. Organ-specific endothelial cell heterogenicity and its impact on regenerative medicine and biomedical engineering applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022;186:114323. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2022.114323 - PubMed
-
- Tombor LS, John D, Glaser SF, Luxán G, Forte E, Furtado M, Rosenthal N, Baumgarten N, Schulz MH, Wittig J, et al. Single cell sequencing reveals endothelial plasticity with transient mesenchymal activation after myocardial infarction. Nat Commun. 2021;12:681. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-20905-1 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zeisberg EM, Tarnavski O, Zeisberg M, Dorfman AL, Mcmullen JR, Gustafsson E, Chandraker A, Yuan X, Pu WT, Roberts AB, et al. Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition contributes to cardiac fibrosis. Nat Med. 2007;13:952–961. doi: 10.1038/nm1613 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

