Research Trends and Hotspots in Female Pattern Hair Loss: A Bibliometric Study
- PMID: 40736064
- PMCID: PMC12309151
- DOI: 10.1111/jocd.70369
Research Trends and Hotspots in Female Pattern Hair Loss: A Bibliometric Study
Abstract
Background: Female pattern hair loss (FPHL) is a common yet understudied condition with significant psychosocial impacts. Understanding global research trends and emerging topics in FPHL is essential for guiding future investigations.
Aims: This bibliometric analysis aimed to provide an overview of key trends, influential contributors, and evolving research themes in FPHL from 1957 to 2024.
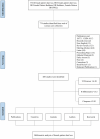
Patients/methods: Publications related to FPHL were retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection. Bibliometric analysis and visualization were performed using VOSviewer, CiteSpace, and the R package "bibliometrix."
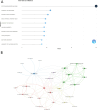
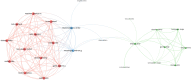
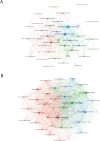
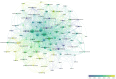
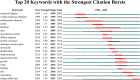
Results: The study analyzed 488 publications authored by 2165 researchers across 189 journals. The USA led in publication output and citations, followed by China and South Korea. Leading institutions included the Egyptian Knowledge Bank, University of Melbourne, and National Taiwan University. Shapiro Jerry was the most prolific author. The Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology had the highest publication count, whereas the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology was the most cited. Keyword analysis identified emerging hotspots, such as "mechanisms," "management," and "safety," with growing interest in "scalp," "association," and "telogen effluvium."
Conclusions: This study highlights the global research landscape of FPHL, emphasizing the focus on treatment efficacy, safety, and underlying mechanisms. Future research may prioritize accurate diagnostic methods and risk factor exploration.
Keywords: CiteSpace; alopecia; bibliometric analysis; female pattern hair loss.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Research status, hotspots and perspectives of artificial intelligence applied to pain management: a bibliometric and visual analysis.Updates Surg. 2025 Jun 28. doi: 10.1007/s13304-025-02296-w. Online ahead of print. Updates Surg. 2025. PMID: 40580377
-
Driving innovations in cancer research through spatial metabolomics: a bibliometric review of trends and hotspot.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 10;16:1589943. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1589943. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40557160 Free PMC article.
-
Global research trends of MicroRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: bibliometrics and visualization analysis.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Jan;44(1):53-66. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-07250-6. Epub 2024 Nov 28. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 39604743
-
The bibliometric and visualization analysis of alcohol-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head: research trends and future directions (1998-2024).J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 Aug 2;20(1):724. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-06138-8. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 40753253 Free PMC article.
-
Research trends on lactate in cancer: a bibliometric analysis and comprehensive review (2015-2024).Front Immunol. 2025 May 9;16:1587867. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1587867. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40416986 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kozicka K., Łukasik A., Pastuszczak M., and Wojas‐Pelc A., “Methods of Treatment Patients With Androgenetic Alopecia Based on Reference of Department of Dermatology in Cracow,” Polski Merkuriusz Lekarski 46, no. 272 (2019): 80–83. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

