Total wrist arthroplasty revisited: survival, function, and patient-reported outcomes of BIAX and universal II prostheses over 15 years
- PMID: 40736718
- PMCID: PMC12310860
- DOI: 10.1007/s00402-025-06005-5
Total wrist arthroplasty revisited: survival, function, and patient-reported outcomes of BIAX and universal II prostheses over 15 years
Abstract
Background: In the management of degenerative osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis of the wrist, surgical intervention remains an important treatment option when conservative approaches such as medication, physiotherapy, and assistive devices prove insufficient. Despite decades of development, no single wrist prosthesis has yet emerged as the definitive standard in total wrist arthroplasty. To address this gap, the German Society for Hand Surgery established the Total Endoprosthesis (TEP) Register in 2004 to systematically collect and evaluate long-term clinical outcomes. The present prospective single-centre study analyses and presents the long-term results of patients enrolled in the TEP register, offering valuable insights into the performance and durability of wrist prostheses in a real-world clinical setting.
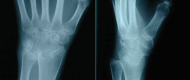
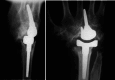
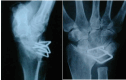
Patients/materials/methods: Between 2000 and 2011, a total of 29 total endoprostheses were implanted in 25 patients in a single centre study due to severe degenerative changes in the wrist. Of these, 22 had rheumatoid arthritis and 3 degenerative osteoarthritis. The prosthesis models BIAX (N = 13) and Universal II (N = 16) were implanted. The present study describes the mean outcome after a mean observation period of 13.8 (1.7-21.4) years for the BIAX prosthesis and 10.5 years (0.2-16.4) for the Universal II prosthesis.
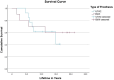
Results: The probability of survival after 15 years is 60% for the BIAX prosthesis and 41% for the Universal II prosthesis. After 21 years, results are only available for the BIAX prosthesis with a value of 60%. The BIAX prosthesis showed a lower complication rate. Subjectively, 15 years postoperatively, the BIAX prosthesis showed a lower mean value in the QuickDASH score (BIAX 33.8%, Universal II 50.3%), lower results in the visual analogue pain scale under stress (BIAX: 1 point; Universal II: 3 points) with higher patient satisfaction (BIAX: 86%; Universal II: 78%).
Conclusion: In conclusion, our observations show that the BIAX prosthesis is superior to the Universal II prosthesis 15 years after surgery in terms of survival probability, complication rate and better results in satisfaction, the visual analogue pain scale and the QuickDASH score.
Keywords: BIAX; Total Wrist Arthroplasty; Universal II.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Mobile bearing vs fixed bearing prostheses for posterior cruciate retaining total knee arthroplasty for postoperative functional status in patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Feb 4;2015(2):CD003130. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003130.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25650566 Free PMC article.
-
What Are the Functional, Radiographic, and Survivorship Outcomes of a Modified Cup-cage Technique for Pelvic Discontinuity?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2149-2160. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003186. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 38991223
-
Retention versus sacrifice of the posterior cruciate ligament in total knee arthroplasty for treating osteoarthritis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Oct 11;2013(10):CD004803. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004803.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 24114343 Free PMC article.
-
What Are the Relative Associations of Surgeon Performance and Prosthesis Quality With THA Revision Rates?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Feb 1;483(2):237-249. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003217. Epub 2024 Aug 6. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 39115546
-
Balneotherapy (or spa therapy) for rheumatoid arthritis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Apr 11;2015(4):CD000518. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000518.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25862243 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Halim A, Weiss AP (2017) Total wrist arthroplasty. J Hand Surg Am 42:198–209 - PubMed
-
- Sivakumar B, Rapisarda A, Freeman H, Xu J, Graham D (2025) Metal-on-metal disease in wrist arthroplasty: a systematic review and proposed management algorithm. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 35(1):126 - PubMed
-
- Gendera H et al (2020) Medium term outcomes of the universal 2 total wrist arthroplasty in patients with degenerative or posttraumatic osteoarthritis of the wrist. Acta Orthop Belg 86(3):549–554 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

