Variation, Overlap, and Stability in Defining Safety Net Hospitals
- PMID: 40736736
- PMCID: PMC12311695
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.23923
Variation, Overlap, and Stability in Defining Safety Net Hospitals
Abstract
Importance: The lack of universally accepted definitions for safety net hospitals (SNHs) has made it difficult to effectively design policies to support these hospitals and the populations they serve.
Objective: To evaluate the overlap, variation, and consistency across different definitions for SNH status.
Design, setting, and participants: This retrospective cohort study used a hospital year-level dataset on short-term acute care US hospitals from 2014 to 2022. Hospital-level and area-level measures were used to define SNHs. Hospital characteristics under each definition, overlap across definitions, and stability of SNH samples produced by each definition from were described. Data analyses were performed from August 2024 to June 2025.
Exposure: Nine hospital-level and 4 area-level SNH definitions.
Main outcomes and measures: Hospital characteristics under each definition, overlap across definitions, and stability of SNH samples over time. Hospital-level definitions included Medicare Disproportionate Share Hospital (DSH) index, Medicare inpatient day share, dual-eligible or low-income subsidy (DLIS) inpatient day share, Medicaid inpatient day share, Medicare Safety-Net Index, teaching status, public ownership, uncompensated care share, and operating margins. Area-level measures included Area Deprivation Index, Social Vulnerability index, proportion Hispanic population, and proportion Black population. Safety net status was assigned based on quartiles defined nationally (or within a state for Medicaid-specific definitions). For a subset of measures, this quartile-based approach was compared between the absolute number of inpatient days attributed to each patient group and the relative number (or share) of inpatient days.
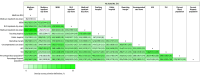
Results: Among 4531 short-term acute care hospitals, between 992 (21.9%) and 1326 (29.3%) were SNHs in 2022, depending on definition. SNHs defined based on the absolute level of inpatient days or absolute level of DLIS populations were often large (51% [242 of 476] or 67% [537 of 801]) and were not often rural (9% [45 of 476] or 2% [17 of 801]). Meanwhile, SNHs defined based on relative level of Medicaid inpatient days or relative level of DLIS patients were more often small (63% [298 of 476] and 82% [660 of 801]) and rural (48% [228 of 476] and 69% [555 of 801]) hospitals. The largest overlap across definitions was between a hospital's Medicaid inpatient day share and Medicare DSH index (55% overlap [808 of 1466 hospitals]), which tended to represent large, teaching hospitals. Public ownership, teaching status, and Medicare DSH index produced the most stable definitions of SNHs over time from 2014 to 2022, with 83% (862 of 1043), 74% (1000 of 1354), and 60% (809 of 1358) of similar hospitals, respectively, meeting safety net criteria. The least stable definitions were based on low operating margins, high uncompensated care share, and high DLIS day share, with only 15% (263 of 1796), 20% (362 of 1823), and 25% (436 of 1725) of similar hospitals, respectively, meeting safety net criteria in 2014, 2018, and 2022.
Conclusions and relevance: In this cohort study of US hospitals, different SNH definitions produced different samples, and candidate measures had variable overlap and stability over time. These findings highlight the trade-offs when considering different options to define SNHs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Institute of Medicine Committee on the Changing Market, Managed Care, and the Future Viability of Safety Net Providers . America’s Health Care Safety Net: Intact but Endangered. National Academies Press; 2000. Accessed June 22, 2020. https://www.nap.edu/download/9612#
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

