Foot Measurements From Three-Dimensional Scans: Elinvision 3DST Reliability
- PMID: 40737191
- PMCID: PMC12309729
- DOI: 10.1002/jfa2.70070
Foot Measurements From Three-Dimensional Scans: Elinvision 3DST Reliability
Abstract
Background: 3D foot scanners such as the Elinvision 3DST foot scanner potentially offer a faster, alternative method to traditional plaster casting to produce orthotics or therapeutic footwear.
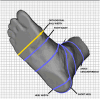
Objective(s): To assess the reliability of 3DST-derived foot length, orthogonal ball width, heel width and ball girth. We also compared 3D scanner and manually derived measures.
Study design: Repeated measures design.
Methods: Two independent raters carried out three scans each of the right foot of 20 healthy participants (10 female) aged 18 years or over (mean age 38 ± 11.4 years) using the 3DST scanner (software v1.6.21.833). Manual foot measurements were taken by an experienced rater using Ritz stick and tape measure.
Results: Intraclass correlation coefficients were excellent for both inter-rater reliability (0.99-1.00, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.97-1.00) and intra-rater reliability (Rater 1: 0.98-1.00, 95% CI 0.96-1.00; Rater 2: 0.97-1.00, 95% CI 0.94-1.00). Standard error of the mean ranged from 0.1 to 0.4 cm both for scanner and manual measurements. The mean absolute differences between the scanner and manual measurements were ≤ 0.4 cm for foot length, orthogonal ball width (0.2-0.3 cm), ball girth and heel width (0.3-0.4 cm) but larger for foot waist, short heel, ankle circumference and anatomical ball width (0.5-1.1 cm).
Conclusions: The 3DST scanner has potential application for capture of basic foot dimensions in footwear fit research. However, larger differences relative to manual measures for other dimensions limits its potential in orthotics or therapeutic footwear production.
Keywords: 3D scanner; accuracy; foot measurement; footwear; orthosis; reliability.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Foot and Ankle Research published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Australian Podiatry Association and The Royal College of Podiatry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Maden T., Bayramlar K., Maden C., and Yakut Y., “Investigating the Effect of Appropriate Fitting Footwear on Functional Performance Level, Balance and Fear of Falling in Older Adults: A Comparative‐Observational Study,” Geriatric Nursing 42, no. 2 (2021): 331–335, 10.1016/j.gerinurse.2021.01.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alonso‐Montero C., Torres‐Rubio A., Padrós‐Flores N., Navarro‐Flores E., and Segura‐Heras J. V., “Footprint Curvature in Spanish Women: Implications for Footwear Fit,” International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 6 (2020): 1876, 10.3390/ijerph17061876. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

