Evaluating the inhibitory efficacy of Oxalis phytocompounds on monoamine oxidase B: An integrated approach targeting age related neurodegenerative diseases through molecular docking and dynamics simulations
- PMID: 40737296
- PMCID: PMC12309996
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0329168
Evaluating the inhibitory efficacy of Oxalis phytocompounds on monoamine oxidase B: An integrated approach targeting age related neurodegenerative diseases through molecular docking and dynamics simulations
Abstract
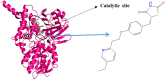
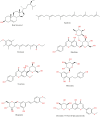
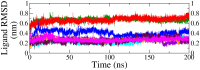
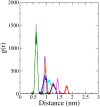
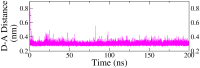
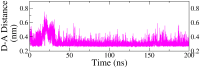
Monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) serves as a critical target in the management of neurodegenerative diseases (NDDs) such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's due to its role in regulating oxidative stress and dopamine metabolism. In this context, phytochemicals from Oxalis species, known for their neuroprotective properties, were explored for their potential MAO-B inhibitory activity using computational approach. Plant-derived compounds, offering a better safety profile than synthetic drugs and greater cost-effectiveness, present a promising avenue for developing alternative therapeutic strategies. Molecular docking (MD), molecular dynamics simulations (MDS), and binding free energy calculations were employed to evaluate the inhibitory potential of Oxalis phytochemicals against MAO-B (PDB ID: 4A79). Stable ligand-protein complexes with optimal docking scores were selected, and key parameters from molecular dynamics trajectories, including binding stability and interactions, were analyzed to identify high potential inhibitors of MAO-B for therapeutic development. Results showed beta-sitosterol (-11.92 kcal/mol), squalene (-11.89 kcal/mol), etretinate (-11.46 kcal/mol), rhoifolin (-11.44 kcal/mol), and swertisin (-11.13 kcal/mol) demonstrated superior binding affinities compared to the native ligand (-11.12 kcal/mol). Three additional compounds; phloridzin (-11.10 kcal/mol), rhapontin (-11.02 kcal/mol), and diosmetin 7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (-10.96 kcal/mol) exhibited better binding than reference drugs. The predominant interactions between protein and ligand were hydrophobic, with hydrogen bonds and Pi-stacking enhancing the complexes' stability. The evaluation based on geometrical and thermodynamic metrics derived from 200 ns MDS, identified rhoifolin, beta-sitosterol, and swertisin as promising MAO-B inhibitors. Minimal translational and rotational movements of these ligands within the catalytic site of MAO-B under quasi-physiological conditions suggested effective inhibition. Preserved thermodynamic feasibility reinforced these findings. ADMET analysis identified squalene and beta-sitosterol as CNS active candidates with favorable pharmacokinetics, while etretinate, rhoifolin, and swertisin may act as peripheral modulators, requiring optimization for improved CNS delivery. Further experimental validation of efficacy, pharmacokinetics, and safety is recommended to advance the therapeutic potential of these hit candidates.
Copyright: © 2025 Shrestha et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Integrative machine learning and molecular simulation approaches identify GSK3β inhibitors for neurodegenerative disease therapy.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21632. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-04129-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40593894 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular screening and dynamics simulation reveal potential phytocompounds in Swertia chirayita targeting the UspA1 protein of Moraxella catarrhalis for COPD therapy.PLoS One. 2025 Feb 28;20(2):e0316275. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0316275. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40019889 Free PMC article.
-
Support vector machine classification-guided identification of novel monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors via structure-based modeling to treat neurodegenerative diseases.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Aug 16;322(Pt 4):146932. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.146932. Online ahead of print. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40825424
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Monoamine oxidase B inhibitors for early Parkinson's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD004898. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004898.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034956 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

