VapC toxins promote the pathogenesis of Rickettsia heilongjiangensis by cleaving essential RNAs from both Rickettsia and its host
- PMID: 40737303
- PMCID: PMC12321070
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1013380
VapC toxins promote the pathogenesis of Rickettsia heilongjiangensis by cleaving essential RNAs from both Rickettsia and its host
Abstract
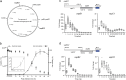
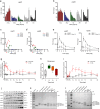
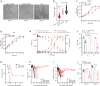
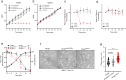
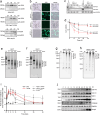
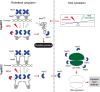
Toxin-antitoxin (TA) modules enable bacteria to persist under stressful environments. However, they are typically absent from host-associated prokaryotes due to their potential host toxicity. Here, the obligate intracellular bacterium spotted fever group (SFG) rickettsiae, which causes mild to severe human illness, was shown to harbor two vapBC TA modules. One of the vapBC modules (vapBC1) is crucial for Rickettsia to withstand accumulated host reactive oxidative species (ROS), via induction of bacterial dormancy through cleavage on the anti-codon loop of tRNAfMet, thereby facilitating intracellular survival and infection in a mouse model. Another vapBC module (vapBC2) was found to be activated and toxin exposed to host cytoplasm, contributing to Rickettsia's virulence and adaptability in its human host by non-specifically degrading host rRNAs rather than regulating rickettsial growth. Recognition of these rickettsial effectors contributes to understanding the intracellular adaptability and pathogenicity of all host-associated pathogens that harbor TA modules.
Copyright: © 2025 Liu et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ser/Thr phosphorylation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis type II RelK toxin by PknK destabilizes TA interaction and interferes with toxin neutralization.mBio. 2025 Jul 9;16(7):e0106825. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01068-25. Epub 2025 Jun 17. mBio. 2025. PMID: 40525867 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella exploits host- and bacterial-derived β-alanine for replication inside host macrophages.Elife. 2025 Jun 19;13:RP103714. doi: 10.7554/eLife.103714. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40536105 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylserine-binding receptor, CD300f, on macrophages mediates host invasion of pathogenic and non-pathogenic rickettsiae.Infect Immun. 2025 Jun 10;93(6):e0005925. doi: 10.1128/iai.00059-25. Epub 2025 May 1. Infect Immun. 2025. PMID: 40310290 Free PMC article.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

