Identification of the T-box transcription factor t-bet in chickens and its role in immune response
- PMID: 40737904
- PMCID: PMC12332921
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105589
Identification of the T-box transcription factor t-bet in chickens and its role in immune response
Abstract
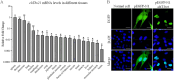
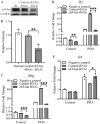
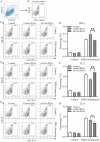
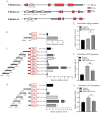
T-bet (T-box transcription factor TBX21), encoded by the Tbx21 gene, is a key regulator of T helper 1 (Th1) cell differentiation and cellular immunity. However, the role of T-bet in avian species remains elusive. To investigate the role of T-bet in avian immune response, we cloned chicken T-bet (chT-bet) from a White Leghorn chicken spleen-derived cDNA library. Multiple sequence alignments and structural analyses revealed that the amino acid sequence of chT-bet has 50.4 % and 51.1 % identity to its human and mouse orthologs, respectively, but the T-box DNA-binding domain remains conserved across species. We found that chT-bet is highly expressed in immune-related organs, particularly the spleen and thymus, and that Newcastle disease virus (NDV) infection significantly upregulated chT-bet expression both in virto and in vivo. Knockdown of chT-bet by RNAi markedly reduced the expression of IFN-γ but not IL-4 in MSB1 cells. Furthermore, chT-bet overexpression in DF-1 cells activated the promoter of IFN-γ while suppressing promoter activation of IL-2 and IL-4. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays confirmed the direct binding of chT-bet to IFN-γ and IL-2 promoters. In contrast, chT-bet's regulation of IL-4 appeared indirect. These findings establish chT-bet as a central orchestrator of Th1 immunity in chickens, directly driving IFN-γ production and regulating IL-2 and IL-4 expressions through distinct pathways, providing insights for vaccine development and disease control strategies.
Keywords: Chicken; Cytokine regulation; T-bet; Th1 immune response.
Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Modulation of T helper 1 and T helper 2 immune balance in a murine stress model during Chlamydia muridarum genital infection.PLoS One. 2020 May 15;15(5):e0226539. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226539. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32413046 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive single-cell chromatin and transcriptomic profiling of peripheral immune cells in nonsegmental vitiligo.Br J Dermatol. 2025 Jun 20;193(1):115-124. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljaf041. Br J Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39888372
-
Analysis of antiviral functions, differences and apoptotic effects of two novel MHC-Iα genotypes in orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides).Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2025 Nov;166:110571. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2025.110571. Epub 2025 Jul 24. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40714287
-
Type 1 Diabetes: A Guide to Autoimmune Mechanisms for Clinicians.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025 Aug;27 Suppl 6(Suppl 6):40-56. doi: 10.1111/dom.16460. Epub 2025 May 15. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025. PMID: 40375390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alteration patterns of peripheral concentrations of cytokines and associated inflammatory proteins in acute and chronic stages of schizophrenia: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Lancet Psychiatry. 2023 Apr;10(4):260-271. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(23)00025-1. Epub 2023 Feb 27. Lancet Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36863384
References
-
- Afkarian M., Sedy J.R., Yang J., Jacobson N.G., Cereb N., Yang S.Y., Murphy T.L., Murphy K.M. T-bet is a STAT1-induced regulator of IL-12R expression in naïve CD4+ T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2002;3:549–557. - PubMed
-
- Amirian M., Jafari-Nozad A.M., Darroudi M., Farkhondeh T., Samarghandian S. Overview of the miR-29 family members’ function in breast cancer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023;230 - PubMed
-
- Bean A.G.D., Lowenthal J.W. In: Chapter 9 - avian Cytokines and Their Receptors. Pages 249–276 in Avian Immunology. Third Edition. Kaspers B., Schat K.A., Göbel T.W., Vervelde L., editors. Academic Press; Boston: 2022.
-
- Bódi I., Minkó K., Molnár D., Nagy N., Oláh I. A novel aspect of the structure of the avian thymic medulla. Cell Tissue Res. 2015;359:489–501. - PubMed
-
- Boyd A.C., Peroval M..Y., Hammond J.A., Prickett M.D., Young J.R., Smith A.L. TLR15 is unique to avian and reptilian lineages and recognizes a yeast-derived agonist. J. Immunol. 2012;189:4930–4938. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

