Cohousing-mediated microbiota transfer promotes bone health and modulates gut integrity, and immunity in young broiler chickens
- PMID: 40737907
- PMCID: PMC12332927
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105587
Cohousing-mediated microbiota transfer promotes bone health and modulates gut integrity, and immunity in young broiler chickens
Abstract
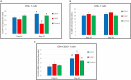
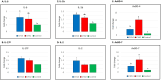
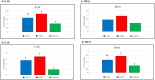
The intestine hosts a complex microbiota, which plays a crucial role in health and development. This study investigated the impact of cohousing day-old broilers with 14-day-old (CH14) or 42-day-old (CH42) broiler chickens and their fecal material for a week, compared to a non-cohoused control group. Birds were raised for 42 days, and bone traits, gut integrity and microbiota, cytokine and antimicrobial peptide profiles, and T cell immunity subsets were assessed at days 14 and 42. Production parameters were recorded weekly, and mortality daily. Both treatment groups exhibited significantly improved tibial bone length, cortical bone volume, and mineral density, with reduced pore volume and diameter. These effects were more pronounced in CH42 birds at day 14. Pro-inflammatory (IL-6, IL-17, IL-1β, IL-2, AvBD-4, AvBD-7) and anti-inflammatory (IL-10, TGF-β) markers were monitored, with CH42 birds showing significantly higher levels of both IL-10 and TGF-β at day 42. CH42 birds had higher CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells and lower CD4+ T cells, while CD8+ T cells remained unchanged. Gut integrity markers (Claudin-2, Occludin, ZO-1, JAM-2) were improved in both groups. CH42 birds showed increased microbiota alpha and beta diversity and Firmicutes dominance by day 42. Cohousing and fecal material transfer improved bone development, gut integrity and microbiota, and immune homeostasis, highlighting the potential of older birds' microbiota and inspiring the development of microbiota-based approaches to enhance poultry health, welfare, and management.
Keywords: Bone health; Broiler; Cohousing; Gut integrity; Immunity.
Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures The authors have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Metagenomic Insight into Cecal Microbiota Shifts in Broiler Chicks Following Eimeria spp. Vaccination.Microorganisms. 2025 Jun 24;13(7):1470. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13071470. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40731980 Free PMC article.
-
Dose and age-dependent effects of Eimeria spp. infection on cytokine and intestinal integrity gene expression in broiler chickens.Vet Parasitol. 2025 Aug;338:110550. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2025.110550. Epub 2025 Jul 23. Vet Parasitol. 2025. PMID: 40716185
-
Mogroside V protects lipopolysaccharides-induced lung inflammation chicken via suppressing inflammation mediated by the Th17 through the gut-lung axis.J Anim Sci. 2025 Jan 4;103:skae388. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae388. J Anim Sci. 2025. PMID: 39716346
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Amin N., Boccardi V., Taghizadeh M., Jafarnejad S. Probiotics and bone disorders: the role of RANKL/RANK/OPG pathway. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2020;32:363–371. - PubMed
-
- Berg C., Sanotra G. Can a modified latency-to-lie test be used to validate gait-scoring results in commercial broiler flocks? Anim. Welf. 2003;12:655–659.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

