A human milk oligosaccharide alters the microbiome, circulating hormones, and metabolites in a randomized controlled trial of older adults
- PMID: 40738103
- PMCID: PMC12432366
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.102256
A human milk oligosaccharide alters the microbiome, circulating hormones, and metabolites in a randomized controlled trial of older adults
Abstract
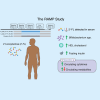
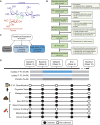
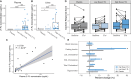
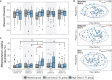
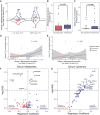
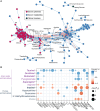
Aging-related immune dysfunction is linked to cancer, atherosclerosis, and neurodegenerative diseases. This 6-week randomized controlled trial evaluated whether 2'-fucosyllactose (2'-FL), a human breast milk oligosaccharide with established benefits in infants and animal models, could improve gut microbiota and immune function in 89 healthy older adults (mean age 67.3 years). While the primary endpoint of cytokine response change was not met, 2'-FL supplementation increased gut Bifidobacterium levels and elevated serum insulin, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, and FGF21 hormone. Bifidobacterium "responders" experienced additional metabolic and proteomic changes and also performed better on a cognitive test of visual memory. Nonresponders were more likely to lack Bifidobacterium in their gut microbiota at the start of the intervention. Multi-omics analysis indicated a systemic response to 2'-FL, which could be detected in blood and urine, showcasing the potential of this prebiotic to provide diverse benefits for healthy aging. This trial was registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03690999).
Keywords: 2'-fucosyllactose; Bifidobacterium; Human milk oligosaccharide; aging; metabolomics; prebiotics.
Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests J.M.C., A.S.-D., and R.H.B. are employees of Abbott Laboratories, which is a commercial manufacturer of nutritional products containing HMOs including infant formula. J.L.S. is a founder, a shareholder, and on the scientific advisory board of Novome Biotechnologies and Interface Biosciences. M.M.C., J.L.S., C.D.G., and Abbott Laboratories have filed a provisional patent application related to this work.
Figures

References
-
- Franceschi C., Bonafè M., Valensin S., Olivieri F., De Luca M., Ottaviani E., De Benedictis G. Inflamm-aging. An evolutionary perspective on immunosenescence. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000;908:244–254. - PubMed
-
- Shen-Orr S.S., Furman D., Kidd B.A., Hadad F., Lovelace P., Huang Y.-W., Rosenberg-Hasson Y., Mackey S., Grisar F.A.G., Pickman Y., et al. Defective Signaling in the JAK-STAT Pathway Tracks with Chronic Inflammation and Cardiovascular Risk in Aging Humans. Cell Syst. 2016;3:374–384.e4. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lynch S.V., Pedersen O. The Human Intestinal Microbiome in Health and Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016;375:2369–2379. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

