The food-associated resistome is shaped by processing and production environments
- PMID: 40739039
- PMCID: PMC12313530
- DOI: 10.1038/s41564-025-02059-8
The food-associated resistome is shaped by processing and production environments
Abstract
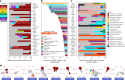
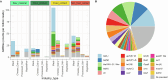
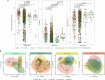
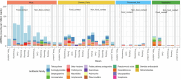
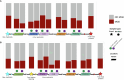
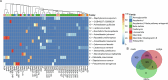
Food production systems may act as transmission routes for antimicrobial-resistant (AMR) bacteria and AMR genes (AMRGs) to humans. However, the food resistome remains poorly characterized. Here 1,780 raw-material (milk, brine, fresh meat and so on), end-product (cheese, fish, meat products and vegetables) and surface (processing, cooling, smoking, ripening and packing rooms) samples from 113 food processing facilities were subjected to whole-metagenome sequencing. Assembly-free analyses demonstrated that >70% of all known AMRGs, including many predicted to confer resistance to critically important antibiotics, circulate throughout food production chains, with those conferring resistance to tetracyclines, β-lactams, aminoglycosides and macrolides being the most abundant overall. An assembly-based analysis highlighted that bacteria from the ESKAPEE group, together with Staphylococcus equorum and Acinetobacter johnsonii, were the main AMRG carriers. Further evaluation demonstrated that ~40% of the AMRGs were associated with mobile genetic elements, mainly plasmids. These findings will help guide the appropriate use of biocides and other antimicrobials in food production settings when designing efficient antimicrobial stewardship policies.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








References
-
- Fisher, M. C., Hawkins, N. J., Sanglard, D. & Gurr, S. J. Worldwide emergence of resistance to antifungal drugs challenges human health and food security. Science360, 739–742 (2018). - PubMed
-
- O’Neill, J. I. M. Antimicrobial resistance: tackling a crisis for the health and wealth of nations. (The Review on Antimicrobial Resistance, 2014); https://amr-review.org/sites/default/files/AMR%20Review%20Paper%20-%20Ta...
-
- WHO: Antimicrobial Resistance, 2023 (WHO, 2024).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

