A composite risk score to identify older adults at high risk of hearing loss in a community screening program
- PMID: 40739219
- PMCID: PMC12312306
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-025-06208-w
A composite risk score to identify older adults at high risk of hearing loss in a community screening program
Abstract
Background: Age-related hearing loss (HL) is highly prevalent among older adults, yet it often goes undetected and untreated. Routine screening in community settings is not widespread, and hearing aid uptake remains very low. We aimed to construct a composite risk score to identify individuals at high risk of HL for targeted audiometric screening.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study using data from a community-based health screening program in Shenzhen, China. Participants underwent pure-tone audiometry at 500-8000 Hz to determine hearing thresholds. Moderate or greater HL was defined as a pure-tone average (PTA) ≥ 35dB in the better ear. Stepwise multivariable regression was used to identify predictors of HL, which were then used to develop a cumulative Hearing Risk Score (HRS).
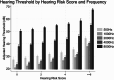
Results: A total of 2,490 adults (mean age, 67.5 years, SD 5.8 years) were included; 32.5% (810 participants) had moderate or greater hearing loss. Of 22 risk factors included in the stepwise regression model, seven were identified: self-reported hearing difficulty, age 65 years or older, male sex, social isolation, cardiovascular disease, and metabolic disease. These were incorporated into the HRS, with total scores ranging from 1 to 23. The HRS was strongly associated with moderate or greater hearing loss, with adjusted odds ratios increasing from 4.50 (95% confidence interval (CI), 1.57-12.88) for a score of 1 to 39.11 (13.50-113.33) for a score of 6 or more (P for trend < 0.001). Similar dose-response patterns were observed at all frequencies tested (0.5 to 8 kHz).
Conclusions: The HRS showed a clear dose-response relationship with HL and may serve as a practical tool to target older adults for confirmatory audiologic evaluation.
Keywords: Hearing loss; Older adults; Risk score; Screening.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study followed the Declaration of Helsinki and informed consent was obtained from the participants. All participants provided informed consent for their health data to be used in research, and the study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Longgang District Ear, Nose and Throat Hospital, Shenzhen. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Extended High-Frequency Thresholds: Associations With Demographic and Risk Factors, Cognitive Ability, and Hearing Outcomes in Middle-Aged and Older Adults.Ear Hear. 2024 Nov-Dec 01;45(6):1427-1443. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0000000000001531. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Ear Hear. 2024. PMID: 38987892 Free PMC article.
-
The association between hearing loss and depression in the China health and retirement longitudinal study.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):20537. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05749-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40595946 Free PMC article.
-
Ventilation tubes (grommets) for otitis media with effusion (OME) in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Nov 15;11(11):CD015215. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015215.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37965944 Free PMC article.
-
Community screening for visual impairment in older people.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 20;2(2):CD001054. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001054.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29460275 Free PMC article.
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- LGKCYLWS2023003/Shenzhen Longgang Innovation of Science and Technology Commission
- LGKCYLWS2023003/Shenzhen Longgang Innovation of Science and Technology Commission
- LGKCYLWS2023003/Shenzhen Longgang Innovation of Science and Technology Commission
- LGKCYLWS2023003/Shenzhen Longgang Innovation of Science and Technology Commission
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

