Strategies to improve academic motivation in undergraduate nursing students in Iran: a qualitative content analysis
- PMID: 40739249
- PMCID: PMC12309027
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-025-07322-z
Strategies to improve academic motivation in undergraduate nursing students in Iran: a qualitative content analysis
Abstract
Background: Academic motivation of nursing students is a broad and multidimensional concept that is a factor in achieving academic success, better quality of learning, creativity, academic satisfaction, reducing anxiety, continuing education and training competent nurses. The most important barrier to learning in nursing education environments is the lack of interest and motivation among students. This study aimed to explore ways to improve academic motivation in nursing students.
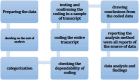
Methods: This qualitative study was conducted in Ramsar City in 2023. A conventional qualitative content analysis was followed to collect data using 14 in-depth individual interviews over a period of 12 months with participants selected through purposive sampling. For data analysis, Lundman and Granheim's method was adopted.
Results: Data analysis led to the extraction of 143 codes, 14 subcategories, 3 categories, and one theme. Strategies to improve academic motivation in nursing students were found to be a subjective, dynamic and multi-dimensional concept divided into two categories: "Improving educational conditions and performance" and "Improving students' welfare and recreational conditions".
Conclusion: Academic motivation is considered one of the essentials of learning and a tool to achieve educational and training goals. By using the strategies to increase academic motivation resulting from this study, an effective step can be taken in this field. Also Understanding these influential strategies can play a significant role in educational and career planning and decision-making, selecting appropriate educational and clinical measures and facilities in the university and students' future work environment, developing educational and career regulations, effective interaction with learners, ultimately increasing the effectiveness of professors' teaching and better teaching and learning activities.
Keywords: Academic motivation; Improvement; Interest; Iran; Learning; Qualitative content analysis; Student nurse.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The paper was part of a larger research project entitled “Investigating ways to improve academic motivation in nursing students: A qualitative content analysis”, reviewed and approved by the ethics committee of the Health Research School - Babol University of Medical Sciences (#IR.MUBABOL.REC.1402.007). Before the interview, the participants received an oral explanation of the purpose of the study, participant rights, freedom to participate in the study, the possibility of not answering questions to the researcher or withdrawing from the interview, and confidentiality of information in all stages of data collection and publication. They were asked to sign a written consent form. The time and place of the interview were agreed on beforehand. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Similar articles
-
Health professionals' experience of teamwork education in acute hospital settings: a systematic review of qualitative literature.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Apr;14(4):96-137. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-1843. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532314
-
Effectiveness and experience of arts-based pedagogy among undergraduate nursing students: a mixed methods systematic review.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Nov;14(11):139-239. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-003188. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27941518
-
The effects of flipped classroom and jigsaw teaching strategies on learning, retention of course content, and satisfaction among nursing students: a quasi-experimental study.BMC Med Educ. 2025 Jul 26;25(1):1118. doi: 10.1186/s12909-025-07662-1. BMC Med Educ. 2025. PMID: 40713652 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
Student and educator experiences of maternal-child simulation-based learning: a systematic review of qualitative evidence.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2017 Nov;15(11):2666-2706. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-003147. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2017. PMID: 29135750
References
-
- Zaheri A, Eshaghi Z, Kheiri S, Ghaderi H. The association of emotional intelligence with academic achievement and academic motivation in students of Shahrekord paramedical school in 2018–2019. Horiz Med Educ Develop. 2021;12(2):32–21.
-
- Ramezani G, Pourbairamian G, Aalaa M, Moradi E, Habibi H, Bigdeli S. Educational motivation improvement strategies for postgraduate students: nominal group technique. Dev Strategies Med Educ. 2021;8(1):1–12.
-
- Yousefi A, Ghassemi G, Firouznia S. The relationship between academic motivation and academic achievement in medical students of Isfahan university of medical sciences. Iran J Med Educ. 2009;9(1):1–7.
-
- Montazeri N, Kianipour N, Nazari B, Ziapour A, Bakhshi S. Health promoting behaviors among university students: A Case-Sectional study of Kermanshah university of medical sciences. Int J Pediatr. 2017;5(6):5091–9. 10.22038/ijp.2017.8631.
-
- Parejo-Jiménez N, Expósito-López J, Chacón-Cuberos R, Olmedo-Moreno EM. Critical thinking and motivation in vocational training and baccalaureate: A comparison study of students of Spanish nationality, unaccompanied foreign minors and young care leavers. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(9):5272. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources