Systematic data management for effective AI-driven decision support systems in robotic rehabilitation
- PMID: 40739308
- PMCID: PMC12310958
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-09740-2
Systematic data management for effective AI-driven decision support systems in robotic rehabilitation
Abstract
Robotic rehabilitation is becoming a standard in post-stroke physical rehabilitation, and these setups, often coupled with virtual exercises, collect a large and finely grained amount of data about patients' motor performance, in terms of kinematics and force interactions. Given the high resolution of data throughout the rehabilitation treatment, invaluable information is concealed, especially if oriented towards predictive systems and decision support systems. Nevertheless, a comprehensive understanding of how manipulating these datasets with machine-learning to produce such outputs is still missing. This study leverages comprehensive robotic-assisted rehabilitation data to systematically investigate clinical outcome predictions (FMA, ARAT and MI) and robot parameters suggestions based solely on kinematic and demographic data. Our method significantly outperforms conventional approaches on both tasks demonstrating the potential of systematic data handling in advancing rehabilitation practices. Moreover, under the explainable-AI policies, a focus on prediction power of variables and a clinical knowledge base of predicted outcome are provided.
Keywords: Decision support system; Deep neural networks; Kinematics; Machine learning; Post-stroke; Regression; Rehabilitation; Robotics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The author(s) declare no competing interests.
Figures
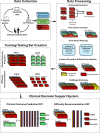
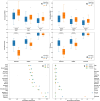
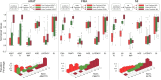


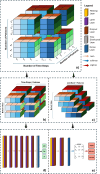
References
-
- Khalid, S., Alnajjar, F., Gochoo, M., Renawi, A. & Shimoda, S. Robotic assistive and rehabilitation devices leading to motor recovery in upper limb: a systematic review. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol.18(5), 658–672 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Wu, J., Cheng, H., Zhang, J., Yang, S. & Cai, S. Robot-assisted therapy for upper extremity motor impairment after stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Phys. Ther.101(4), 010 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Aprile, I. et al. Upper limb robotic rehabilitation after stroke: a multicenter, randomized clinical trial. J. Neurol. Phys. Ther.44(1), 3–14 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Schwarz, A., Kanzler, C. M., Lambercy, O., Luft, A. R. & Veerbeek, J. M. Systematic review on kinematic assessments of upper limb movements after stroke. Stroke50(3), 718–727 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

