Inhibition of inner ear macrophage phagocytosis alleviates cisplatin-induced ototoxicity
- PMID: 40739377
- PMCID: PMC12311119
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-025-08525-7
Inhibition of inner ear macrophage phagocytosis alleviates cisplatin-induced ototoxicity
Abstract
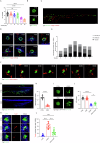
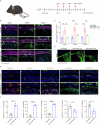
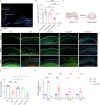
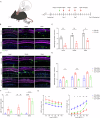
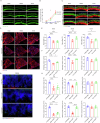
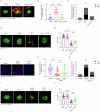
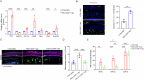
The immune response is considered a significant pathological mechanism of inner ear damage. However, the role of macrophages, as key components of immune cells, in immunity in the inner ear remains elusive. Evidence from other organs indicates that phagocytosis, a core function of macrophages, plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis, development, and tissue repair regeneration. However, it has rarely been studied in the inner ear. This field may currently hold new insights. In this study, we aimed to investigate the immunological contribution of resident macrophages in the inner ear to cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. By using clodronate liposomes and cytochalasin to deplete macrophages or inhibit macrophage phagocytosis locally, we first elucidated the dynamic changes in the immune state of inner ear macrophages during cisplatin injury through multimodal and multidimensional approaches. High-spatiotemporal-resolution single-cell analysis and real-time imaging of macrophages during zebrafish hair cell death identified proinflammatory subsets during cisplatin injury. We found that macrophage activation through phagocytosis synergized with the inflammatory response and that inhibiting macrophage phagocytosis could ameliorate cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Finally, we discuss how the highly plastic phagocytic function of resident macrophages in the inner ear holds potential for the development of strategies for treating cisplatin-induced hearing loss.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: All animal experiments conducted in this study are approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Sun Yat-sen University. We have complied with all relevant ethical regulations for animal use.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Macrophage depletion protects against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity.Sci Adv. 2024 Jul 26;10(30):eadk9878. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adk9878. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 39047106 Free PMC article.
-
Topical antiseptics for chronic suppurative otitis media.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Jun 9;6(6):CD013055. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013055.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40484403
-
Vernonia amygdalina displays otoprotective effects via antioxidant pathway on cisplatin-induced hair cell loss in zebrafish.Arch Toxicol. 2025 Jul;99(7):2993-3005. doi: 10.1007/s00204-025-04038-8. Epub 2025 Mar 30. Arch Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40159305
-
Medical interventions for the prevention of platinum-induced hearing loss in children with cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jul 1;(7):CD009219. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009219.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24984156
-
Platinum-induced hearing loss after treatment for childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 3;2016(8):CD010181. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010181.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27486906 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang, X. et al. Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: From signaling network to therapeutic targets. Biomed. Pharmacother.157, 114045 (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81970887/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 2025A1515010422/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Guangdong Natural Science Foundation)
- 2025A1515012388/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (Guangdong Natural Science Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

