Regulation of Notch signaling by multiple Ankyrin repeat containing protein Mask
- PMID: 40739510
- PMCID: PMC12309132
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-025-02190-3
Regulation of Notch signaling by multiple Ankyrin repeat containing protein Mask
Abstract
Background: Notch pathway is an evolutionarily conserved, highly pleiotropic signaling system that governs diverse developmental processes. Its diverse functions are attributed to the intricate regulatory mechanisms that finely tune the pathway. While several known elements contribute to maintaining cellular homeostasis by modulating Notch signaling, many unidentified components likely play significant roles in its regulation, necessitating further exploration.
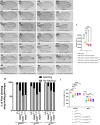
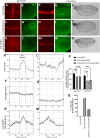
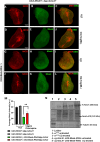
Methods: To identify novel regulators of Notch-intracellular domain (Notch-ICD), we carried out a yeast two-hybrid screen and identified Multiple Ankyrin repeat single KH domain containing protein (Mask) as an interacting partner of Notch-ICD. Physical interaction between these two proteins was further validated by co-immunoprecipitation experiments. Moreover, cellular studies using immunocytochemistry reveals that Mask plays important role in Notch turnover and protect from degradation. To inhibit lysosomal degradation, chloroquine was introduced in the food at a concentration of 1 mg/ml.
Results: Immunocytochemical analyses revealed that Notch and Mask co-localised within the same subcellular compartments. Different alleles of mask showed strong genetic interactions with Notch pathway components in transheterozygous combinations. Loss- and gain-of-function studies of Mask demonstrated that it plays a regulatory role in Notch signaling. Specifically, the absence of Mask results in downregulation of Notch target genes, although it does not significantly affect endogenous Notch protein levels. Our data suggest that Mask positively regulates Notch signaling by stabilizing Notch-ICD and protecting it from lysosomal degradation. Treatment with 1 mg/ml chloroquine can mitigate the Mask loss-mediated Notch intracellular domain degradation. This study presents a novel mode of Notch signaling regulation mediated by the Ankyrin repeat-containing protein Mask.
Conclusion: Here we provide evidence that Mask physically binds with Notch-ICD and positively regulates Notch signaling pathway by protecting it from degradation. Mask genetically interacts with Notch and Notch pathway components and absence of Mask affects the Notch signaling pathway thus it may control the hyper activation of the signaling.
Keywords: Drosophila; Ankyrin repeat; Cell signaling; Endocytosis; Mask; Notch.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Regulation of Notch signaling by miR-79 in Drosophila eye development.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025 Aug 30;776:152222. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2025.152222. Epub 2025 Jun 21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025. PMID: 40561754
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Drosophila histone variant H2Av facilitates Notch signaling activity in a two-tier regulatory fashion.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Jul 1;23(1):322. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02333-6. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40598498 Free PMC article.
-
Stress-induced Cdk5 activity enhances cytoprotective basal autophagy in Drosophila melanogaster by phosphorylating acinus at serine437.Elife. 2017 Dec 11;6:e30760. doi: 10.7554/eLife.30760. Elife. 2017. PMID: 29227247 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid closed-loop systems for managing blood glucose levels in type 1 diabetes: a systematic review and economic modelling.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Dec;28(80):1-190. doi: 10.3310/JYPL3536. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39673446 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersson ER, Sandberg R, Lendahl U. Notch signaling: simplicity in design, versatility in function. Development. 2011;138:3593–612. - PubMed
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD, Lake RJ. Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science. 1999;284:770–6. - PubMed
-
- Baron M, Aslam H, Flasza M, Fostier M, Higgs J, Mazaleyrat S, Wilkin M. Multiple levels of Notch signal regulation. Mol Membr Biol. 2002;19:27–38. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

