Prevalence, characteristics, and outcomes of patients with low baseline C-reactive protein in giant cell arteritis
- PMID: 40739573
- PMCID: PMC12312337
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-025-03594-9
Prevalence, characteristics, and outcomes of patients with low baseline C-reactive protein in giant cell arteritis
Abstract
Objective: Elevated inflammatory markers play a crucial role in the diagnosis and follow-up of patients with giant cell arteritis (GCA). This study aimed to describe the prevalence, characteristics, and outcomes of patients with low baseline (< 10 mg/L) C-reactive protein (CRP) in GCA.
Methods: A retrospective observational study was conducted at Lille University Hospital, involving all patients diagnosed with GCA between January 2000 and April 2023. Patients were categorized based on their CRP level at diagnosis. Baseline characteristics, clinical manifestations, laboratory findings, imaging results, and outcomes were compared between patients with baseline CRP < 10 mg/L ("low CRP") and those with CRP ≥ 10 mg/L ("high CRP").
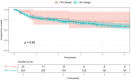
Results: Of the 380 patients, 7.6% (n = 29) had baseline CRP < 10 mg/L at diagnosis. When compared to the high CRP group, the low CRP group exhibited a lower incidence of fever, and had a higher incidence of ocular involvement, particularly anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (28% vs. 13%, p = 0.04), and limb claudication (24% vs. 8%, p < 0.01). Plasma fibrinogen levels were elevated (> 4 g/L) in 77% of patients with low CRP. Despite differences in clinical presentation, relapse rates were equilibrated between the two groups.
Conclusion: GCA patients with low CRP are not rare and present with more ocular and peripheral vascular involvement and less constitutional symptoms in our study. Elevated fibrinogen in these patients suggests active inflammation despite low CRP. Clinicians should consider GCA even with a CRP < 10 mg/L, as these patients may present with severe complications.
Keywords: Acute phase reactant; C reactive protein; Giant cell arteritis; Vasculitis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Putman MS, Gribbons KB, Ponte C, et al. Clinicopathologic associations in a large international cohort of patients with giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2022;74:1013–8. 10.1002/acr.24540. - PubMed
-
- Hellmich B, Agueda A, Monti S, et al. 2018 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of large vessel vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79:19–30. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215672. - PubMed
-
- Ponte C, Grayson PC, Robson JC, et al. 2022 American college of rheumatology/eular classification criteria for giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022;74:1881–9. 10.1002/art.42325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous