Notch2 improves granulosa cell functions in premature ovarian failure by activating the Wnt2/β-catenin pathway
- PMID: 40739650
- PMCID: PMC12308925
- DOI: 10.1186/s13048-025-01745-9
Notch2 improves granulosa cell functions in premature ovarian failure by activating the Wnt2/β-catenin pathway
Abstract
Background: Notch2 and Wnt2/β-catenin pathway improve granulosa cell (GC) functions, and there are interactions between Notch and Wnt/β-catenin in some cells. We aimed to investigate whether Notch2 improves GC functions in premature ovarian failure (POF) by activating the Wnt2/β-catenin pathway.
Methods: Notch2 expression was interfered in mice or KGN cells, then, mice were treated with cyclophosphamide and busulfan intraperitoneally, and KGN cells were exposed to cyclophosphamide to establish POF models. In vivo, the number of follicles at different stages was counted, and interactions between Notch2 and Wnt2 were detected. In vitro, cell viability and cycle were measured. Additionally, hormone levels, oxidative stress (OS) degrees, cell apoptosis, Notch2 and Wnt2/β-catenin pathway-related genes were detected in vivo and in vitro. Finally, Wnt/β-catenin pathway inhibitor (IWR-1), agonist (SKL2001) and β-catenin knockdown were used.
Results: Notch2 overexpression not only improved hormone levels, follicular development, OS degree and ovarian cell apoptosis, but also activated Wnt2/β-catenin pathway for POF mice. Moreover, Notch2 interacted with Wnt2 in POF mice. In vitro, Notch2 knockdown decreased cell viability, disrupted cell cycle, increased cell apoptosis, worsened hormone levels, promoted OS degree and inhibited Wnt2/β-catenin pathway for POF. Importantly, the protective effects of Notch2 overexpression and the worsening impacts of Notch2 knockdown on POF were reversed by IWR-1 and SKL2001. β-Catenin knockdown further impaired GC functions in POF models that underwent Notch2 and β-catenin knockdown.
Conclusion: Notch2 may improve GC functions in POF by activating the Wnt2/β-catenin pathway, suggesting that the Notch2-mediated Wnt2/β-catenin pathway is a novel therapeutic target for POF.
Keywords: Cyclophosphamide; Granulosa cell functions; Notch2; Premature ovarian failure; Wnt2/β-catenin pathway.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All animal experiments were approved by the Laboratory Animal Management and Ethics Committee of Hangzhou Hunter Testing Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (SYXK(Zhe)2024-0003) and strictly adhered to the guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

 P < 0.05 and
P < 0.05 and 
 P < 0.01 vs. Control; #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 vs. oe-NC; @P < 0.05 and @@P < 0.01 vs. oe-Notch2. Results were presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD)
P < 0.01 vs. Control; #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 vs. oe-NC; @P < 0.05 and @@P < 0.01 vs. oe-Notch2. Results were presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD)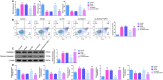
 P < 0.05 and
P < 0.05 and 
 P < 0.01 vs. Control; #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 vs. oe-NC; @P < 0.05 and @@P < 0.01 vs. oe-Notch2. Results were presented as mean ± SD
P < 0.01 vs. Control; #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 vs. oe-NC; @P < 0.05 and @@P < 0.01 vs. oe-Notch2. Results were presented as mean ± SD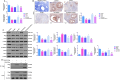
 P < 0.05 and
P < 0.05 and 
 P < 0.01 vs. Control; #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 vs. oe-NC; @P < 0.05 and @@P < 0.01 vs. oe-Notch2. Results were presented as mean ± SD
P < 0.01 vs. Control; #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 vs. oe-NC; @P < 0.05 and @@P < 0.01 vs. oe-Notch2. Results were presented as mean ± SD
 P < 0.05 and
P < 0.05 and 
 P < 0.01 vs. Normal;
P < 0.01 vs. Normal;  P < 0.05 and
P < 0.05 and 
 P < 0.01 vs. Control; *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 vs. Model; #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 vs. sh-NC; @P < 0.05 and @@P < 0.01 vs. sh-Notch2. Results were presented as mean ± SD
P < 0.01 vs. Control; *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 vs. Model; #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 vs. sh-NC; @P < 0.05 and @@P < 0.01 vs. sh-Notch2. Results were presented as mean ± SD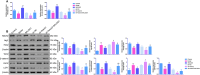
 P < 0.05 and
P < 0.05 and 
 P < 0.01 vs. Control; *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 vs. Model; #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 vs. sh-NC; @P < 0.05 and @@P < 0.01 vs. sh-Notch2. Results were presented as mean ± SD
P < 0.01 vs. Control; *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 vs. Model; #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 vs. sh-NC; @P < 0.05 and @@P < 0.01 vs. sh-Notch2. Results were presented as mean ± SD
 P < 0.05 and
P < 0.05 and 
 P < 0.01 vs. Model; #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 vs. sh-Notch2 + SKL2001 + sh-NC. Results were presented as mean ± SD
P < 0.01 vs. Model; #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 vs. sh-Notch2 + SKL2001 + sh-NC. Results were presented as mean ± SD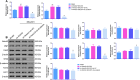
Similar articles
-
TRIB3 regulates Cx43 expression in human granulosa cells via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway: an in vitro study.J Ovarian Res. 2025 Jul 2;18(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s13048-025-01694-3. J Ovarian Res. 2025. PMID: 40605006 Free PMC article.
-
The up-regulation of RIPK3 mediated by ac4C modification promotes oxidative stress-induced granulosa cell senescence by inhibiting the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.IUBMB Life. 2025 Jan;77(1):e2944. doi: 10.1002/iub.2944. IUBMB Life. 2025. PMID: 39865380
-
H3K27ac-induced RHOXF2 activates Wnt2/β-catenin pathway by binding to HOXC13 to aggravate the malignant progression of triple negative breast cancer.Cell Signal. 2024 Aug;120:111196. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111196. Epub 2024 Apr 30. Cell Signal. 2024. PMID: 38697448
-
Interventions for fertility preservation in women with cancer undergoing chemotherapy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Jun 19;6(6):CD012891. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012891.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40536056 Review.
-
Effectiveness of different treatment modalities for the management of adult-onset granulosa cell tumours of the ovary (primary and recurrent).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Apr 21;2014(4):CD006912. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006912.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24753008 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu F, Wang X, Zhao M, Zhang K, Li C, Lin H, et al. Ghrelin alleviates inflammation, insulin resistance, and reproductive abnormalities in mice with polycystic ovary syndrome via the TLR4-NF-κB signaling pathway. Discov Med. 2024;36:946–58. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

