Calprotectin Level and Its Relationship with Right Ventricular Function in Patients with Pulmonary Embolism
- PMID: 40740209
- PMCID: PMC12305831
- DOI: 10.6515/ACS.202507_41(4).20250224F
Calprotectin Level and Its Relationship with Right Ventricular Function in Patients with Pulmonary Embolism
Abstract
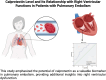
Background: This research sought to assess the role of calprotectin as a biomarker in patients with pulmonary embolism (PE) and to explore its correlation with established biomarkers such as D-dimer, troponin, and pro brain natriuretic peptide (BNP). In addition, we examined the correlation between calprotectin level and right ventricular (RV) function in patients with PE.
Methods: This prospective study was conducted between January 2022 and December 2023 and included 58 patients diagnosed with acute PE and 31 age- and sex-matched controls. Calprotectin level, renal function, hematological parameters, demographic characteristics, and echocardiographic parameters were recorded. For the PE patients, additional data on troponin, D-dimer, high-sensitivity troponin T (hs-troponin T), blood gas analysis, and Pulmonary Embolism Severity Index scores were also collected.
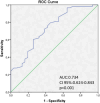
Results: The patients with PE had significantly higher calprotectin, urea, creatinine and leukocyte levels compared to the controls, as well as lower platelet count (p < 0.001). A calprotectin cut-off level of 1.555 mcg/ml could predict PE with 73% sensitivity and 62% specificity in receiver operating characteristic curve analysis. Elevated calprotectin levels were associated with worse RV function, as evidenced by lower tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion and right ventricular systolic myocardial velocity measurements. Correlation analysis revealed that calprotectin levels were inversely related to tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (r = -0.315, p = 0.016) and RV systolic myocardial velocity (r = -0.290, p = 0.027). While calprotectin was not correlated with D-dimer or hs-troponin T, it had a weak correlation with proBNP (r = 0.271, p = 0.04).
Conclusions: This study emphasizes the potential of calprotectin as a valuable biomarker in PE, providing additional insights into RV dysfunction. Although further research is needed to fully establish its clinical utility, calprotectin, which was weakly correlated with proBNP in this study, could complement existing biomarkers such as proBNP and hs-troponin T in the evaluation and management of PE.
Keywords: Cardiac troponin T; Heart failure; Pulmonary embolism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest
Figures
References
-
- Freund Y, Cohen-Aubart F, Bloom B. Acute pulmonary embolism: a review. JAMA. 2022;328:1336–1345. - PubMed
-
- Duffett L, Castellucci LA, Forgie MA. Pulmonary embolism: update on management and controversies. BMJ. 2020;370:m2177. - PubMed
-
- Kaptein FHJ, Kroft LJM, Hammerschlag G, et al. Pulmonary infarction in acute pulmonary embolism. Thromb Res. 2021;202:162–169. - PubMed
-
- Pay L, Çetin T, Keskin K, et al. Prognostic value of pulmonary artery diameter/aorta diameter ratio in patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Herz. 2024;49:464–471. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
