A Single Centre Cross-Sectional Observational Study on Dermatoscopy of Oral Mucosal Disorders and Histopathological Correlation in Tertiary Care Centre from Central India
- PMID: 40740406
- PMCID: PMC12306889
- DOI: 10.4103/ijd.ijd_1145_23
A Single Centre Cross-Sectional Observational Study on Dermatoscopy of Oral Mucosal Disorders and Histopathological Correlation in Tertiary Care Centre from Central India
Abstract
Background: A dermatoscope is a non-invasive diagnostic imaging tool that enables to visualise superficial, deeper structures, pigmentary and vascular patterns of skin, nails, hair and mucosa. Oral mucosal lesions are abnormal alterations in colour, surface, presence of swelling, or loss of integrity of mucosal and semimucosal surface. The use of dermoscopy in the characterisation of mucosal disorder is a grey area and needs further exploration.
Aim: To describe clinical and mucoscopic features and correlate histopathologically in oral mucosal diseases.
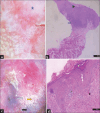
Method: Single-centre, cross-sectional, observational study presenting to inpatient and outpatient departments of dermatology, and otorhinolaryngology. Patients fulfilling inclusion criteria were dermoscopically evaluated using DermLite DL4, 30 mm lens system and 10× magnification and documented in a prestructured proforma. Then, a mucosal biopsy was taken from the visualized site.
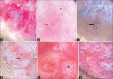
Results: Fordyce spots were observed as white-yellow clods with dots. Median rhomboid glossitis as atrophic filiform papillae at the centre with normal-looking peripheral papillae. Pemphigus vulgaris visualized as a red structureless area, red dots, with violaceous streaks at the periphery. Lichen planus showed a tricolor pattern, Wickham's striae, blunted tips of lingual papillae, discoid lupus erythematosus showed superficial erosions, yellow-white scale, brown pigment spots at the periphery with telangiectasia and follicular plugs at the vermilion border. Aphthous stomatitis characterised by three zones with a central yellowish-white structureless area, a surrounding white area, and a peripheral red structureless area. Actinic cheilitis showed superficial ulceration, polymorphic vessels and white scales. Warts have hyperkeratotic pointed tips with fused bases, with central thrombosed capillaries. Molluscum contagiosum showed a central pore-like structure with crown vessels. Vitiligo showed a white structureless area, a diffuse white glow with a scalloped margin. Premalignant conditions such as oral submucosal fibrosis and leukoplakia showed atrophic lingual papillae, chrysalis white structureless area, with telangiectasia and white to pink structureless area, surface corrugation, white clods and dotted vessels. Limitations in our study were a response to therapy could not be assessed and the relation with the disease activity could not be determined. Difficult-to-reach sites such as the palate, and retromolar area were not assessed. Haziness while capturing pictures due to mist formation hindered the quality of images. Not many premalignant and malignant diseases were recruited to provide the mucoscopy features in predicting the risk of conversion.
Conclusion: Mucoscopy helps in delineating various mucosal diseases with subtle features.
Keywords: Dermoscopy; histopathology; mucosa; mucoscopy; oral mucosal lesions; semimucosa.
Copyright: © 2025 Indian Journal of Dermatology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Micali G, Lacarrubba F. Augmented diagnostic capability using videodermatoscopy on selected infectious and non-infectious penile growths. Int J Dermatol. 2011;50:1501–5. - PubMed
-
- Kumar Jha A, Vinay K, Sławińska M, Sonthalia S, Sobjanek M, Kamińska-Winciorek G, et al. Application of mucous membrane dermoscopy (mucoscopy) in diagnostics of benign oral lesions-literature review and preliminary observations from International Dermoscopy Society study. Dermatol Ther. 2021;34:e14478. - PubMed
-
- Ghodsi SZ, Bahrololoumi Bafruee N, Chams Davatchi C, Rosendahl C, Akay BN, Davatchi F, et al. Dermatoscopic and mucoscopic features of lesions in patients with Behcet's disease. Acta Reumatol Port. 2019;44:225–31. - PubMed
-
- Kaur D, Kaur T, Malhotra SK. Dermoscopic Patterns of Oral Mucosal Lesions: New Dimensions To Mucoscopy. Semantic Scholar. [[Last accessed on 2023 May 06]]. Available from: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/DERMOSCOPIC-PATTERNS-OF-ORAL-MUCOS... .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
