PMab-322: a novel anti-hippopotamus podoplanin monoclonal antibody for multiple applications
- PMID: 40740468
- PMCID: PMC12307670
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2025.102170
PMab-322: a novel anti-hippopotamus podoplanin monoclonal antibody for multiple applications
Abstract
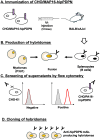
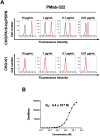
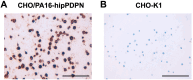
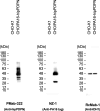
Podoplanin (PDPN) is a highly glycosylated type I transmembrane protein. PDPN expression is observed in various normal tissues, including lymphatic endothelial cells, kidney podocytes, and type I alveolar epithelial cells in the lungs. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) targeting PDPN across different animal species have facilitated the identification of PDPN-positive cells. To date, we have developed anti-PDPN mAbs for over 20 species. These antibodies suit various applications, including flow cytometry, immunoblotting, and immunohistochemistry. In this study, we generated an anti-hippopotamus PDPN (hipPDPN) mAb, PMab-322 (mouse IgG2a, kappa), using the Cell-Based Immunization and Screening (CBIS) method. PMab-322 exhibited strong reactivity to hipPDPN-overexpressed Chinese hamster ovary-K1 and demonstrated moderate affinity (K D: 4.4 × 10-8 M) in a flow cytometry-based measurement. PMab-322 specifically recognizes hipPDPN but does not cross-react with PDPN from 23 other species. Furthermore, PMab-322 successfully detected hipPDPN in both immunoblotting and immunohistochemistry. These findings highlight the potential of PMab-322 for pathological analyses of hippopotamus-derived tissues.
Keywords: CBIS method; Flow cytometry; Hippopotamus podoplanin; Immunoblotting; Immunohistochemistry; Monoclonal antibody.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Hirakawa S., Hong Y.K., Harvey N., Schacht V., Matsuda K., Libermann T., Detmar M. Identification of vascular lineage-specific genes by transcriptional profiling of isolated blood vascular and lymphatic endothelial cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2003;162:575–586. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)63851-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Petrova T.V., Mäkinen T., Mäkelä T.P., Saarela J., Virtanen I., Ferrell R.E., Finegold D.N., Kerjaschki D., Ylä-Herttuala S., Alitalo K. Lymphatic endothelial reprogramming of vascular endothelial cells by the Prox-1 homeobox transcription factor. Embo j. 2002;21:4593–4599. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf470. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

