Molecular and therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on autoimmune diseases
- PMID: 40740529
- PMCID: PMC12305160
- DOI: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i7.107202
Molecular and therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on autoimmune diseases
Abstract
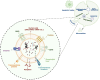
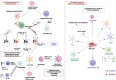
Autoimmune diseases are complex clinical conditions that present significant therapeutic challenges due to their intricate immunological mechanisms. Conventional treatment strategies, such as immunosuppressive drugs and anti-inflammatory therapies, often demonstrate limited efficacy and are associated with considerable side effects. Recently, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have attracted growing interest as a promising therapeutic approach, owing to their immunomodulatory properties and ability to promote tissue repair. However, the direct application of MSCs faces several limitations, including the risk of immunogenicity and difficulties in large-scale production. In this context MSC-derived exosomes (MSC-Exos), nano-sized extracellular vesicles secreted by MSCs, have emerged as a compelling alternative to cell-based therapies. Enriched with proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, these exosomes exhibit potent anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects. Their primary mechanisms of action include enhancing the population of regulatory T cells, modulating macrophage polarization, and suppressing proinflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α. The therapeutic potential of MSC-Exos extends beyond individual conditions, encompassing a wide range of autoimmune diseases. For instance in Behçet's disease, they have been shown to regulate vasculitis and inflammatory processes by inhibiting proinflammatory cytokines and promoting endothelial cell regeneration. Moreover, MSC-Exos have demonstrated promising immunomodulatory effects in other autoimmune diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis. Through mechanisms such as inflammation suppression, vascular repair, and the restoration of immune homeostasis, MSC-Exos represent a versatile and innovative approach to autoimmune disease therapy. This review explored the molecular and therapeutic effects of MSCs and MSC-Exos in autoimmune diseases, with particular emphasis on their clinical potential in Behçet's disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis.
Keywords: Autoimmune diseases; Behçet’s disease; Exosomes; Immunomodulation; Mesenchymal stem cells; Multiple sclerosis; Rheumatoid arthritis; Systemic lupus erythematosus.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
"Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (MSC-exosomes) in hematology: From mechanisms to clinical breakthroughs".Cell Immunol. 2025 Aug;414:104986. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2025.104986. Epub 2025 Jun 3. Cell Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40499318 Review.
-
Comparative Efficacy of Exosomes Derived from Different Mesenchymal Stem Cell Sources in Osteoarthritis Models: An In Vitro and Ex Vivo Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 6;26(12):5447. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125447. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40564912 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Emerging Therapies for Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jul 2;20:8547-8565. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S526945. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40620684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal Stem-Cell-Derived Exosomes and MicroRNAs: Advancing Cell-Free Therapy in Systemic Sclerosis.Cells. 2025 Jul 3;14(13):1018. doi: 10.3390/cells14131018. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40643538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: a promising alternative in the therapy of preeclampsia.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Feb 5;15(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03652-0. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38317195 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Davidson A, Diamond B. Autoimmune diseases. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:340–350. - PubMed
-
- Wang L, Wang FS, Gershwin ME. Human autoimmune diseases: a comprehensive update. J Intern Med. 2015;278:369–395. - PubMed
-
- Mastrandrea LD. An Overview of Organ-Specific Autoimmune Diseases Including Immunotherapy. Immunol Invest. 2015;44:803–816. - PubMed
-
- Pineton de Chambrun M, Wechsler B, Geri G, Cacoub P, Saadoun D. New insights into the pathogenesis of Behçet's disease. Autoimmun Rev. 2012;11:687–698. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

