Swallow Reaction Time in Healthy Adults
- PMID: 40740608
- PMCID: PMC12308766
- DOI: 10.1044/2023_persp-22-00221
Swallow Reaction Time in Healthy Adults
Abstract
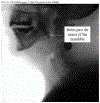
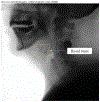
Purpose: Swallow onset is commonly characterized by bolus location. Quantifying this swallow event using swallow reaction time (SRT) may further inform swallow assessment, but few studies have established normative reference values for SRT using a large sample size and well-tested, standardized, and validated videofluoroscopic swallow study (VFSS) approach. The purpose of this study was to investigate SRT in a large cohort of healthy adults and the effects of demographic (age, sex) and bolus (viscosity, volume) characteristics on SRT using the Modified Barium Swallow Impairment Profile approach.
Method: Archival VFSSs of 195 healthy adults (21-89 years) were analyzed to obtain SRT across seven standardized swallow tasks ranging from thin to extremely thick liquid and a solid. Descriptive statistics were generated for age, sex, viscosity, and volume. Generalized estimating equation models were computed to explore the effects of demographic and bolus characteristics on SRT.
Results: Variability in SRT was observed among healthy adults across all swallow tasks. Only viscosity significantly influenced SRT. Specifically, thicker viscosities resulted in longer SRT.
Conclusions: Wide variability in SRT was observed in this large cohort of healthy adults across various liquid swallow tasks and a solid task. Thicker viscosities, in particular, yielded longer SRT and should be considered a normal variant. This study further provides normative SRT data related to a commonly used VFSS approach, which clinicians can use as reference values for their patient data.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The authors have declared that no competing financial or nonfinancial interests existed at the time of publication.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
