Parents' learning support and school attitudes in relation to adolescent academic identity and school performance in nine countries
- PMID: 40740658
- PMCID: PMC12306645
- DOI: 10.1007/s10212-024-00827-4
Parents' learning support and school attitudes in relation to adolescent academic identity and school performance in nine countries
Abstract
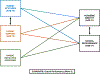
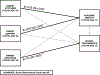
An important question for parents and educators alike is how to promote adolescents' academic identity and school performance. This study investigated relations among parental education, parents' attitudes toward their adolescents' school, parental support for learning at home, and adolescents' academic identity and school performance over time and in different national contexts. Longitudinal data were collected from adolescents and their parents in nine countries (China, Colombia, Italy, Jordan, Kenya, the Philippines, Sweden, Thailand, and the United States). When adolescents were 16 years old, their mothers (N = 1,083) and fathers (N = 859) provided data. When adolescents were 17 years old, 1,049 adolescents (50% girls), and their mothers (N = 1,001) and fathers (N = 749) provided data. Multiple-group path analyses indicated that, across cultures, higher parent education was associated with better adolescent school performance. Parents' attitudes toward their adolescents' school and parent support for learning in the home were not associated with adolescents' school performance but were associated with academic identity. The findings suggest somewhat different pathways to school performance versus academic identity. Implications for helping parents and educators in different countries promote adolescents' academic identity and achievement are discussed.
Keywords: Parents’ learning support; academic identity; adolescent; cross-cultural; parents’ school attitude; school performance.
Figures

References
-
- Abdullah AG, Seedee R, Alzaidiyeen NJ, Al-Shabatat A, Alzeydeen HK, & AlAwabdeh A. (2011). An investigation of teachers’ attitudes towards parental involvement. Educational Research, 2(8), 1402–1408.
-
- Achenbach TM (1991). Integrative guide for the 1991 CBCL 14–18, YSR, and TRF profiles. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.
-
- Al-Rawwad T, Al-Taj H, & Al-Tal S. (2016). Parental involvement and their children’s social adjustment: Evidence from Jordanian students. International Review of Social Sciences and Humanities, 11, 119–125.
-
- Berti C, Mameli C, Speltini G, & Molinari L. (2016). Teacher justice and parent support as predictors of learning motivation and visions of a just world. Issues in Educational Research, 26, 543–560.
-
- Bogunovi B, & Poloving N. (2007). Educational-material context of the family and students’ attitude towards schooling. Zbornik Instituta za Pedagoska Istrazivanja, 39(1), 7–19.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
