Coronal dimmings and what they tell us about solar and stellar coronal mass ejections
- PMID: 40740692
- PMCID: PMC12304066
- DOI: 10.1007/s41116-025-00041-4
Coronal dimmings and what they tell us about solar and stellar coronal mass ejections
Abstract
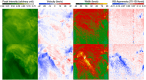
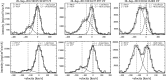
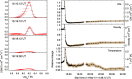
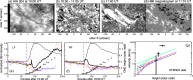
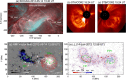
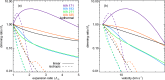
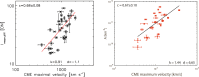
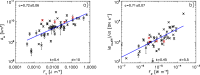
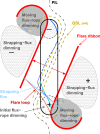
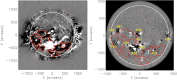
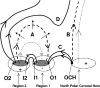
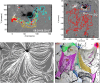
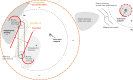
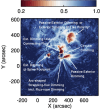
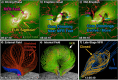
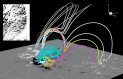
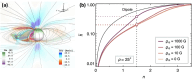
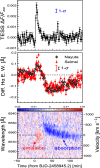
Coronal dimmings associated with coronal mass ejections (CMEs) from the Sun have gained much attention since the late 1990s when they were first observed in high-cadence imagery of the SOHO/EIT and Yohkoh/SXT instruments. They appear as localized sudden decreases of the coronal emission at extreme ultraviolet (EUV) and soft X-ray (SXR) wavelengths, that evolve impulsively during the lift-off and early expansion phase of a CME. Coronal dimmings have been interpreted as "footprints" of the erupting flux rope and also as indicators of the coronal mass loss by CMEs. However, these are only some aspects of coronal dimmings and how they relate to the overall CME/flare process. The goal of this review is to summarize our current understanding and observational findings on coronal dimmings, how they relate to CME simulations, and to discuss how they can be used to provide us with a deeper insight and diagnostics of the triggering of CMEs, the magnetic connectivities and coronal reconfigurations due to the CME as well as the replenishment of the corona after an eruption. In addition, we go beyond a pure review by introducing a new, physics-driven categorization of coronal dimmings based on the magnetic flux systems involved in the eruption process. Finally, we discuss the recent progress in studying coronal dimmings on solar-like and late-type stars, and how to use them as a diagnostics for stellar coronal mass ejections and their properties.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s41116-025-00041-4.
Keywords: Corona; Coronal mass ejections; Flares; Solar physics; Stellar activity; Stellar physics.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Figures


























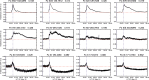

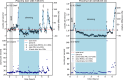
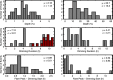

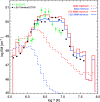

References
-
- Aarnio AN, Matt SP, Stassun KG (2012) Mass loss in pre-main-sequence stars via coronal mass ejections and implications for angular momentum loss. Astrophys J 760(1):9. 10.1088/0004-637X/760/1/9. arXiv:1209.6410 [astro-ph.SR] - DOI
-
- Acton LW (2018) Recalibration of the soft X-ray telescope onboard Yohkoh. Sol Phys 293(10):137. 10.1007/s11207-018-1361-y - DOI
-
- Airapetian VS, Barnes R, Cohen O et al (2020) Impact of space weather on climate and habitability of terrestrial-type exoplanets. Int J Astrobiol 19(2):136–194. 10.1017/S1473550419000132. arXiv:1905.05093 [astro-ph.EP] - DOI
-
- Alvarado-Gómez JD, Drake JJ, Cohen O et al (2018) Suppression of coronal mass ejections in active stars by an overlying large-scale magnetic field: a numerical study. Astrophys J 862(2):93. 10.3847/1538-4357/aacb7f. arXiv:1806.02828 [astro-ph.SR] - DOI
-
- Alvarado-Gómez JD, Drake JJ, Moschou SP et al (2019) Coronal response to magnetically suppressed CME events in M-dwarf stars. Astrophys J Lett 884(1):L13. 10.3847/2041-8213/ab44d0. arXiv:1909.04092 [astro-ph.SR] - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
