Retrospective analysis of systemic lupus erythematosus patients with latent tuberculosis infection: A 5-year follow-up study
- PMID: 40740694
- PMCID: PMC12309263
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jctube.2025.100553
Retrospective analysis of systemic lupus erythematosus patients with latent tuberculosis infection: A 5-year follow-up study
Abstract
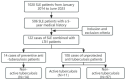
Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) have a higher incidence of tuberculosis (TB)infection compared to the general healthy population. The use of glucocorticoids and immunosuppressive agents for SLE management further elevates TB risk. This study aimed to evaluate the prevalence of latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) in SLE patients and explore risk factors for progression to active TB (ATB) in those with concurrent SLE and LTBI. We conducted a retrospective analysis of SLE patients treated at the Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, Peking University Shenzhen Hospital, between 2014 and 2023. During a five - year follow - up period, LTBI was detected in 122 patients (24.11%). Of these, 11 individuals (all from the subgroup of 108 patients who did not receive tuberculosis preventive treatment [TPT]) progressed to ATB. A comparative analysis between the 11 ATB cases and 111 non-progressing LTBI patients revealed significant differences: ATB cases showed higher cyclophosphamide (CTX) usage, elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) levels, and less frequent hydroxychloroquine (HCQ)administration. These findings underscore the need for regular monitoring during prolonged CTX therapy, especially in moderate-to-high TB burden regions, and highlight the potential protective role of HCQ.
Keywords: Co-infection; Latent tuberculosis infection; Retrospective study; Risk factors; Systemic lupus erythematosus.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Latent Tuberculosis Screening and Active Tuberculosis Disease Development in People Living with HIV: A Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study in Turkiye.Curr HIV Res. 2025;23(1):69-75. doi: 10.2174/011570162X349937250206073759. Curr HIV Res. 2025. PMID: 39945250
-
Performance of eight serum cytokine/chemokine biomarkers in discriminating between active and latent tuberculosis infection in Ghana.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 6;16:1600712. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1600712. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40547033 Free PMC article.
-
Accurate diagnosis of latent tuberculosis in children, people who are immunocompromised or at risk from immunosuppression and recent arrivals from countries with a high incidence of tuberculosis: systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2016 May;20(38):1-678. doi: 10.3310/hta20380. Health Technol Assess. 2016. PMID: 27220068 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic vasculitis with latent tuberculosis infection and associated factors: a cross-sectional multicenter study.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Mar;44(3):1269-1277. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-07279-7. Epub 2025 Jan 21. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 39838164 Free PMC article.
-
Rifamycins (rifampicin, rifabutin and rifapentine) compared to isoniazid for preventing tuberculosis in HIV-negative people at risk of active TB.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jul 5;2013(7):CD007545. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007545.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23828580 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gergianaki I., Fanouriakis A., Repa A., Tzanakakis M., Adamichou C., Pompieri A., et al. Epidemiology and burden of systemic lupus erythematosus in a Southern European population: data from the community-based lupus registry of Crete, Greece. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(12):1992–2000. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211206. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous